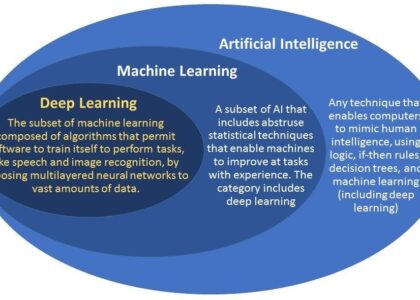
The Importance of Qualitative Data in Statistics
Statistics play a crucial role in various fields, providing valuable insights and understanding through data analysis. While quantitative data, such as numbers and measurements, is commonly used in statistical analysis, qualitative data also holds significant importance.
What is Qualitative Data?
Qualitative data refers to non-numerical information that describes qualities or characteristics. This type of data is often collected through observations, interviews, surveys, or focus groups. Unlike quantitative data, which can be measured and counted, qualitative data provides a deeper understanding of the underlying reasons and motivations behind certain phenomena.
The Role of Qualitative Data in Statistics
Qualitative data adds richness and context to statistical analysis by offering insights into the thoughts, feelings, and experiences of individuals. It helps researchers interpret the meaning behind numerical findings and provides a more comprehensive understanding of complex issues.
Qualitative data is particularly useful in exploratory research, where the goal is to gain a deeper understanding of a subject before developing hypotheses or conducting further quantitative studies. By capturing subjective viewpoints and narratives, qualitative data allows researchers to explore nuances and uncover hidden patterns that may not be apparent through quantitative analysis alone.
Benefits of Using Qualitative Data
- Richness: Qualitative data provides detailed insights into human behaviour, attitudes, and perceptions.
- Context: It helps contextualise quantitative findings within real-world situations and social contexts.
- In-depth Understanding: Qualitative data allows researchers to delve deeper into complex issues and explore underlying motivations.
- New Perspectives: It can reveal new perspectives and ideas that may not emerge from quantitative analysis alone.
- Data Triangulation: Combining qualitative and quantitative data (data triangulation) enhances the validity and reliability of research findings.
In Conclusion
Incorporating qualitative data into statistical analysis enriches research outcomes by providing a holistic view of the subject under study. By embracing both qualitative and quantitative approaches, researchers can gain a more comprehensive understanding of complex phenomena and make informed decisions based on robust evidence.
Enhancing Statistical Insights: Seven Essential Tips for Managing Qualitative Data
- Ensure data quality by validating sources and maintaining accuracy.
- Use appropriate sampling methods to gather diverse and representative data.
- Thoroughly analyse qualitative data using coding and thematic analysis techniques.
- Consider the context in which the data was collected to understand its significance.
- Maintain confidentiality and anonymity of participants to uphold ethical standards.
- Document the research process meticulously for transparency and reproducibility.
- Use qualitative data to complement quantitative findings for a comprehensive analysis.
Ensure data quality by validating sources and maintaining accuracy.
To ensure the quality of qualitative data in statistical analysis, it is essential to validate sources and maintain accuracy throughout the data collection process. By verifying the credibility and reliability of sources, researchers can enhance the trustworthiness of their findings and minimise potential biases. Additionally, maintaining accuracy in data collection and recording procedures helps uphold the integrity of the research outcomes, enabling robust analysis and meaningful interpretations. Validating sources and prioritising accuracy are fundamental steps in ensuring the overall quality and reliability of qualitative data in statistical studies.
Use appropriate sampling methods to gather diverse and representative data.
To ensure the validity and reliability of qualitative data in statistical analysis, it is essential to employ appropriate sampling methods that gather diverse and representative data. By using sampling techniques that encompass a wide range of perspectives and characteristics, researchers can capture the richness and complexity of the subject under study. This approach not only enhances the robustness of the findings but also ensures that the insights derived from the qualitative data are reflective of the broader population or phenomenon being examined. Ultimately, selecting suitable sampling methods is crucial in obtaining comprehensive and meaningful qualitative data that can drive informed decision-making and deepen understanding in statistical analysis.
Thoroughly analyse qualitative data using coding and thematic analysis techniques.
To ensure a comprehensive understanding of qualitative data in statistics, it is essential to conduct thorough analysis employing coding and thematic analysis techniques. Coding involves systematically categorising and labelling data to identify patterns and themes within the information collected. Thematic analysis, on the other hand, focuses on identifying key themes or concepts that emerge from the data, allowing researchers to uncover meaningful insights and draw connections between different elements. By utilising these analytical methods effectively, researchers can extract rich and valuable information from qualitative data, enhancing the depth and quality of statistical analysis.
Consider the context in which the data was collected to understand its significance.
When analysing qualitative data in statistics, it is essential to consider the context in which the data was collected to fully comprehend its significance. The circumstances, environment, and conditions under which the data was gathered can greatly influence the interpretations and conclusions drawn from the analysis. By understanding the context of data collection, researchers can better appreciate the nuances and complexities inherent in qualitative data, leading to more accurate and insightful findings.
Maintain confidentiality and anonymity of participants to uphold ethical standards.
In the realm of statistics, a crucial tip for handling qualitative data is to prioritise the maintenance of confidentiality and anonymity of participants. Upholding ethical standards in research is paramount to ensure the protection and privacy of individuals contributing their insights and experiences. By safeguarding the identities of participants, researchers demonstrate respect for their rights and build trust, fostering a conducive environment for open and honest data collection. This practice not only upholds ethical integrity but also promotes a sense of security among participants, encouraging them to share their perspectives freely without fear of repercussions.
Document the research process meticulously for transparency and reproducibility.
Documenting the research process meticulously is a crucial tip when working with qualitative data in statistics. By keeping detailed records of data collection methods, analysis procedures, and decision-making processes, researchers ensure transparency and reproducibility in their work. Transparent documentation not only enhances the credibility of the research but also allows other researchers to replicate the study and verify its findings. This practice promotes trust in the research outcomes and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field of statistics.
Use qualitative data to complement quantitative findings for a comprehensive analysis.
Utilising qualitative data alongside quantitative findings is essential for conducting a comprehensive analysis in statistics. By incorporating qualitative insights, researchers can delve deeper into the underlying reasons and meanings behind numerical results, providing a richer understanding of the subject matter. Qualitative data adds context, nuance, and depth to statistical analysis, enabling researchers to uncover hidden patterns, explore diverse perspectives, and enhance the overall validity and reliability of their research findings.