Understanding Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Artificial Intelligence
The fields of machine learning, deep learning, and artificial intelligence (AI) are revolutionising industries across the globe. These technologies are not only advancing rapidly but also transforming the way we interact with the world around us. This article aims to demystify these concepts and explore their applications.
Artificial Intelligence: The Big Picture
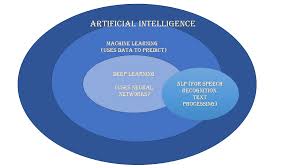
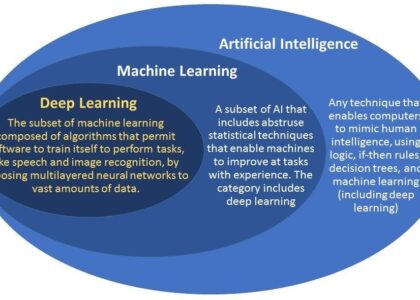
Artificial Intelligence is a broad field that encompasses various technologies designed to simulate human intelligence processes by machines. These processes include learning, reasoning, problem-solving, perception, and language understanding. AI is often divided into two categories: narrow AI, which is designed for specific tasks like voice recognition or image classification; and general AI, which aims to perform any intellectual task a human can do.
Machine Learning: The Heart of AI
Machine learning is a subset of AI that focuses on the development of algorithms that allow computers to learn from and make predictions based on data. Instead of being explicitly programmed to perform a task, machine learning systems use patterns and inference to improve their performance over time. This approach is particularly useful in situations where it’s impractical or impossible to write detailed instructions for every possible scenario.
Types of Machine Learning
- Supervised Learning: Involves training a model on a labelled dataset, meaning that each training example is paired with an output label.
- Unsupervised Learning: Involves training a model on data without labelled responses and finding hidden patterns or intrinsic structures in input data.
- Semi-supervised Learning: Combines both labelled and unlabelled data for training – typically a small amount of labelled data with a large amount of unlabelled data.
- Reinforcement Learning: Involves training models to make sequences of decisions by rewarding them for correct actions over time.
Deep Learning: A Step Further
Deep learning is a specialised subfield of machine learning inspired by the structure and function of the brain’s neural networks. It involves algorithms known as artificial neural networks with many layers (hence “deep”) that can learn increasingly abstract representations from raw data inputs.
This approach has proven extremely effective in tasks such as image recognition, natural language processing (NLP), and autonomous driving systems due to its ability to handle vast amounts of complex data. Unlike traditional machine learning models that often plateau in performance as more data becomes available, deep learning models generally improve with more information.
The Impact on Industries
The integration of AI technologies into various sectors has led to unprecedented advancements:
- Healthcare: AI systems assist in diagnostics through image analysis, predict patient outcomes using historical health records, and personalise treatment plans.
- Finance: Machine learning algorithms detect fraudulent activities by analysing transaction patterns while automating trading strategies based on market trends.
- Manufacturing: Predictive maintenance powered by AI helps reduce downtime by anticipating equipment failures before they occur.
- Agriculture: Deep learning models analyse satellite images for precision farming practices such as crop monitoring and yield prediction.
The Future Outlook
The future holds immense potential for further integration of these technologies into everyday life. As computational power increases alongside advancements in algorithmic research within fields like deep reinforcement learning or generative adversarial networks (GANs), we can expect even more sophisticated applications emerging across diverse domains.
The journey towards fully realised general artificial intelligence remains ongoing; however current developments continue pushing boundaries towards creating intelligent systems capable not only performing specific tasks but understanding contextually complex scenarios akin human cognition levels eventually paving way new era technological innovation reshaping societal norms beyond imagination today!
Exploring Machine Learning, Deep Learning, and Artificial Intelligence: Key Differences, Training Methods, Applications, Neural Networks, and Job Automation Impact
- What is the difference between machine learning, deep learning, and artificial intelligence?
- How are machine learning algorithms trained?
- What are some real-world applications of deep learning technology?
- Can you explain the concept of neural networks in artificial intelligence?
- What impact does artificial intelligence have on job automation?
What is the difference between machine learning, deep learning, and artificial intelligence?
One frequently asked question in the realm of machine learning, deep learning, and artificial intelligence is: What is the difference between these three concepts? Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that focuses on developing algorithms allowing computers to learn from data and make predictions without being explicitly programmed. Deep learning, on the other hand, is a specialised form of machine learning inspired by neural networks in the human brain, utilising multiple layers to learn complex patterns from raw data. Artificial intelligence encompasses a broader scope, aiming to simulate human-like intelligence in machines through various technologies and approaches. While machine learning and deep learning are specific techniques within AI, artificial intelligence encapsulates a wider range of capabilities and applications in mimicking human cognitive functions.
How are machine learning algorithms trained?
Machine learning algorithms are trained through a process that involves feeding them with labelled data, allowing the algorithm to learn patterns and relationships within the data. The training phase typically consists of presenting the algorithm with a set of input data along with the corresponding correct output or target. The algorithm then adjusts its internal parameters iteratively to minimise the difference between its predicted output and the actual target. This iterative process, known as ‘learning’, continues until the algorithm can make accurate predictions on new, unseen data. Training machine learning algorithms is crucial in enabling them to generalise well and perform effectively in real-world applications.
What are some real-world applications of deep learning technology?
Deep learning technology has found numerous real-world applications across various industries, showcasing its transformative potential. In the field of healthcare, deep learning is being used for medical image analysis, enabling more accurate diagnoses and treatment planning. In autonomous driving systems, deep learning algorithms power object detection and recognition, enhancing road safety. Retail companies leverage deep learning for personalised recommendations and customer behaviour analysis to improve marketing strategies. Additionally, in finance, deep learning models are utilised for fraud detection and risk assessment to safeguard financial transactions. These practical applications highlight the versatility and impact of deep learning technology in addressing complex challenges and driving innovation in diverse sectors.
Can you explain the concept of neural networks in artificial intelligence?
Neural networks are a cornerstone concept in artificial intelligence, particularly within the realm of deep learning. Inspired by the structure and functioning of the human brain, neural networks consist of interconnected layers of nodes, or “neurons,” which process data by assigning weights to inputs and passing them through activation functions. The architecture typically involves an input layer, one or more hidden layers, and an output layer. As data passes through these layers, the network adjusts the weights based on error rates from predictions to improve accuracy—a process known as training. This ability to learn from data makes neural networks exceptionally powerful for tasks such as image recognition, natural language processing, and more complex problem-solving scenarios. By mimicking cognitive processes, they enable machines to identify patterns and make decisions with minimal human intervention.
What impact does artificial intelligence have on job automation?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is significantly impacting job automation by transforming the nature of work across various industries. While AI-driven automation can increase efficiency and productivity, leading to cost savings for businesses, it also has the potential to displace certain jobs, particularly those involving routine and repetitive tasks. However, rather than simply eliminating jobs, AI is reshaping the workforce by creating new opportunities and roles that require advanced skills in technology management, data analysis, and machine learning development. As a result, there is an increasing demand for reskilling and upskilling workers to adapt to this changing landscape. Ultimately, while AI may automate some aspects of jobs, it also fosters innovation and drives economic growth by enabling humans to focus on more complex and creative tasks.