Understanding AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning
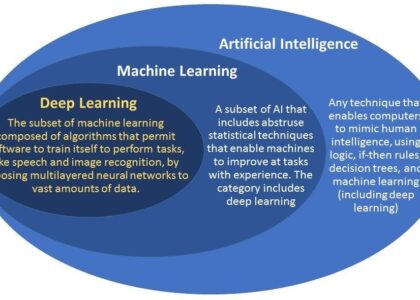
The fields of Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning have become pivotal in shaping the future of technology. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they represent different concepts within the realm of computer science. Understanding their distinctions is crucial for anyone looking to explore the potential of these technologies.
Artificial Intelligence: The Broad Concept
Artificial Intelligence is a broad field that aims to create machines capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence. These tasks include reasoning, problem-solving, understanding natural language, and perceiving the environment. AI encompasses a wide range of technologies and approaches, from rule-based systems to advanced neural networks.
Machine Learning: A Subset of AI
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that focuses on developing algorithms that allow computers to learn from and make predictions or decisions based on data. Instead of being explicitly programmed for specific tasks, ML systems improve their performance as they are exposed to more data over time. This ability to learn and adapt makes ML particularly powerful in dynamic environments.
Types of Machine Learning
- Supervised Learning: In this approach, algorithms are trained on labelled datasets, meaning that each training example is paired with an output label. The model learns to map inputs to outputs based on this training data.
- Unsupervised Learning: Here, algorithms work with unlabelled data and attempt to identify patterns or structures within it. Clustering and association are common techniques used in unsupervised learning.
- Semi-supervised Learning: This method combines both labelled and unlabelled data during training. It is particularly useful when acquiring a fully labelled dataset is expensive or time-consuming.
- Reinforcement Learning: In reinforcement learning, algorithms learn by interacting with an environment and receiving feedback in the form of rewards or punishments. This approach is often used in robotics and game playing.
Deep Learning: A Revolution Within ML
Deep Learning is a specialised branch of machine learning inspired by the structure and function of the human brain’s neural networks. It involves using multi-layered neural networks to model complex patterns in large amounts of data. Deep learning has been instrumental in achieving breakthroughs in image recognition, natural language processing, speech recognition, and more.
The key advantage of deep learning models lies in their ability to automatically extract features from raw data without manual intervention. This capability has led to significant advancements across various domains such as autonomous driving, healthcare diagnostics, and personalised recommendations.
The Interconnected Future
The synergy between AI, machine learning, and deep learning continues to drive technological innovation at an unprecedented pace. As these fields evolve further, they hold immense potential for transforming industries by improving efficiency, accuracy, and decision-making processes.
The future promises even more sophisticated applications as researchers push the boundaries of what machines can achieve through intelligent computation. Understanding these technologies today will be essential for anyone looking to harness their power tomorrow.
Frequently Asked Questions: Understanding AI, ML, and Deep Learning
- Is it worth studying AI and ML?
- What are the 3 domains of AI?
- What is difference between AI and ML?
- What is the difference between AI ML DL and DS?
- What is the difference between AI ML and DL?
- Should I learn ML or AI first?
- Is ML required for deep learning?
- What are the 4 types of AI?
- Is ML the same as deep learning?
Is it worth studying AI and ML?
Studying AI and ML is undoubtedly worth it, given the profound impact these technologies are having across various sectors. As industries increasingly rely on data-driven decision-making, the demand for professionals skilled in AI and ML continues to grow. These fields offer exciting opportunities to be at the forefront of innovation, whether it’s developing intelligent systems that can automate mundane tasks or creating advanced models that predict complex patterns. Furthermore, expertise in AI and ML is not only applicable to technology companies but is also becoming invaluable in healthcare, finance, automotive industries, and more. As such, acquiring knowledge and skills in these areas can significantly enhance one’s career prospects and provide a competitive edge in the job market.
What are the 3 domains of AI?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be broadly categorised into three primary domains: Artificial Narrow Intelligence (ANI), Artificial General Intelligence (AGI), and Artificial Superintelligence (ASI). Artificial Narrow Intelligence, also known as weak AI, refers to systems designed to perform a specific task or a narrow range of tasks. These systems operate under a limited set of constraints and are prevalent in applications such as voice assistants and recommendation engines. Artificial General Intelligence, or strong AI, is the hypothetical ability of an AI system to understand, learn, and apply intelligence across a wide array of tasks at a level comparable to human cognitive abilities. While AGI remains largely theoretical at this stage, it represents the goal of creating machines with comprehensive cognitive capabilities. Lastly, Artificial Superintelligence surpasses human intelligence in all aspects—scientific creativity, general wisdom, and social skills. ASI is purely speculative at present but raises important ethical considerations about the future role of machines in society.
What is difference between AI and ML?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are closely related, yet they represent distinct concepts within the field of computer science. AI is the broader concept that encompasses the development of systems capable of performing tasks that would typically require human intelligence, such as reasoning, problem-solving, and understanding language. It includes a wide range of techniques and technologies designed to simulate human cognitive processes. On the other hand, ML is a subset of AI focused specifically on developing algorithms that enable computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed for each task. While AI provides the overarching goal of creating intelligent systems, ML offers a pathway to achieve this by allowing machines to learn from experiences and adapt to new inputs autonomously.
What is the difference between AI ML DL and DS?
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), Deep Learning (DL), and Data Science (DS) are interconnected fields, yet each has its distinct focus and scope. AI is the overarching domain that aims to create systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as decision-making and language understanding. Within AI, ML is a subset that involves developing algorithms allowing computers to learn from data and improve over time without being explicitly programmed. DL, a further subset of ML, uses neural networks with multiple layers to analyse complex patterns in large datasets, excelling in areas like image and speech recognition. On the other hand, Data Science is a broader discipline that encompasses the extraction of insights from data using various techniques, including statistics, ML, and data analysis. While DS often employs AI and ML tools to process and interpret data, its primary goal is to derive actionable insights from vast amounts of information across diverse fields.
What is the difference between AI ML and DL?
Artificial Intelligence (AI), Machine Learning (ML), and Deep Learning (DL) are interconnected fields within computer science, each with distinct roles. AI is the overarching concept that aims to create machines capable of mimicking human intelligence, encompassing a wide range of technologies and methods. Machine Learning, a subset of AI, focuses on developing algorithms that allow computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed for specific tasks. Within ML, Deep Learning represents a specialised area that uses multi-layered neural networks to model complex patterns in large datasets. While ML can involve various techniques like decision trees or support vector machines, DL specifically leverages neural networks inspired by the human brain’s architecture to achieve remarkable accuracy in tasks such as image and speech recognition. Thus, while all three aim to enhance machine intelligence, DL is a more advanced technique under the broader ML umbrella within the expansive field of AI.
Should I learn ML or AI first?
When deciding whether to learn Machine Learning (ML) or Artificial Intelligence (AI) first, it’s important to understand the relationship between the two. AI is a broad field encompassing various technologies and methodologies aimed at creating intelligent systems capable of performing tasks that require human-like intelligence. ML, on the other hand, is a subset of AI focused specifically on developing algorithms that enable computers to learn from data. For beginners, starting with AI can provide a comprehensive overview of the field and its diverse applications, setting a solid foundation for understanding where ML fits within this landscape. However, if you are particularly interested in data-driven decision-making and predictive modelling, diving directly into ML might be more beneficial as it offers practical skills that are highly sought after in today’s job market. Ultimately, your choice should align with your interests and career goals, as both fields offer valuable insights and opportunities.
Is ML required for deep learning?
Machine Learning (ML) is indeed a foundational element for deep learning, as deep learning is essentially a specialised subset of ML. While machine learning encompasses a broad range of algorithms and techniques for enabling computers to learn from data, deep learning specifically focuses on using neural networks with multiple layers to model complex patterns. Therefore, understanding the principles of ML provides essential groundwork for delving into deep learning. It equips one with the necessary knowledge of data handling, algorithmic thinking, and evaluation methods that are crucial when working with deep neural networks. In essence, while one can directly study deep learning concepts, having a solid grasp of machine learning fundamentals greatly enhances comprehension and effective application in the field of deep learning.
What are the 4 types of AI?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) can be categorised into four distinct types, each representing a different level of capability and functionality. The first type is *Reactive Machines*, which are the most basic form of AI systems. They are designed to perform specific tasks without any memory or ability to use past experiences to inform current decisions. An example of this is IBM’s Deep Blue, the chess-playing computer. The second type is *Limited Memory* AI, which builds upon reactive machines by incorporating some historical data to make more informed decisions. Many modern AI applications, such as self-driving cars, fall into this category as they use past data to navigate roads safely. The third type is *Theory of Mind* AI, which remains largely theoretical at this stage. It refers to systems that can understand human emotions and intentions, allowing for more sophisticated interactions between humans and machines. Finally, the fourth type is *Self-aware AI*, which represents the pinnacle of AI development—a hypothetical future where machines possess consciousness and self-awareness akin to human beings. While self-aware AI currently exists only in science fiction, it remains a topic of significant interest and debate among researchers and ethicists alike.
Is ML the same as deep learning?
The question of whether Machine Learning (ML) is the same as Deep Learning often arises in discussions about artificial intelligence. While both fall under the umbrella of AI, they are not synonymous. Machine Learning is a broader concept that encompasses various techniques for enabling computers to learn from data and make predictions. Deep Learning, on the other hand, is a subset of ML that specifically involves neural networks with multiple layers to model complex patterns. In essence, Deep Learning is a sophisticated approach within the realm of Machine Learning, showcasing the depth and complexity achievable in training algorithms to perform tasks that mimic human cognition.