The Role of Data Analysis in Qualitative Research
Qualitative research is a method used to gain insights into people’s beliefs, attitudes, behaviours, and experiences. It involves collecting non-numerical data such as interviews, observations, and open-ended survey responses. Data analysis in qualitative research is a crucial step that helps researchers make sense of the information gathered and draw meaningful conclusions.
Understanding Qualitative Data Analysis
Unlike quantitative research that focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, qualitative research deals with rich, descriptive data that requires a different approach to analysis. Qualitative data analysis involves systematically categorising, interpreting, and making sense of the collected information to identify patterns, themes, and relationships.
Methods of Qualitative Data Analysis
There are various methods used in qualitative data analysis, including:
- Thematic Analysis: Involves identifying themes or patterns within the data through coding and categorisation.
- Content Analysis: Focuses on identifying specific words or phrases that occur frequently in the data.
- Grounded Theory: A method used to develop theories based on patterns observed in the data.
- Narrative Analysis: Involves analysing the stories or narratives shared by participants to understand their experiences.
The Importance of Data Analysis in Qualitative Research
Data analysis is essential in qualitative research for several reasons:
- Identifying Patterns: Helps researchers identify recurring themes or patterns within the data.
- Gaining Insights: Allows researchers to gain deeper insights into participants’ perspectives and experiences.
- Evidence-Based Findings: Enables researchers to support their findings with concrete evidence from the data.
- Data Interpretation: Assists researchers in interpreting the meaning behind participants’ responses and behaviours.
Challenges in Qualitative Data Analysis
While qualitative data analysis can provide valuable insights, it also comes with challenges such as subjectivity, researcher bias, and the complexity of interpreting nuanced data. Researchers must be diligent in their approach to ensure the credibility and reliability of their findings.
In Conclusion
Data analysis plays a vital role in qualitative research by helping researchers uncover meaningful insights from non-numerical data. By employing rigorous analytical methods and techniques, researchers can make sense of complex information and generate valuable findings that contribute to our understanding of human behaviour and experiences.
Understanding Qualitative Data Analysis: Key Steps, Methods, and Components
- What are the 7 steps of qualitative data analysis?
- What are the 5 methods of qualitative data analysis?
- What is data analysis in qualitative research?
- What are the 4 components of qualitative data analysis?
- What is the data analysis of qualitative research?
What are the 7 steps of qualitative data analysis?
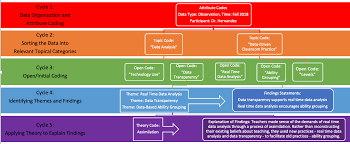
In qualitative research, the process of data analysis typically involves seven key steps to systematically make sense of the collected information. These steps include familiarising oneself with the data, generating initial codes to identify patterns, searching for themes among the codes, reviewing and refining those themes, defining and naming the themes, producing a comprehensive analysis, and finally, reporting the findings. Each step is crucial in uncovering meaningful insights from qualitative data and ensuring that the research outcomes are thorough and well-supported by evidence gathered during the analysis process.
What are the 5 methods of qualitative data analysis?
In qualitative research, there are five main methods of data analysis commonly used to make sense of the collected information. These methods include thematic analysis, content analysis, grounded theory, narrative analysis, and phenomenological analysis. Thematic analysis involves identifying recurring themes or patterns within the data, while content analysis focuses on specific words or phrases that emerge frequently. Grounded theory aims to develop theories based on observed patterns, narrative analysis delves into the stories shared by participants, and phenomenological analysis explores the essence of lived experiences. Each method offers a unique approach to analysing qualitative data and contributes to a deeper understanding of research findings.
What is data analysis in qualitative research?
Data analysis in qualitative research is the process of systematically examining and interpreting non-numerical data collected through methods such as interviews, observations, and open-ended survey responses. It involves identifying patterns, themes, and relationships within the data to uncover meaningful insights into participants’ beliefs, attitudes, behaviours, and experiences. Qualitative data analysis aims to make sense of the rich, descriptive information gathered during the research process by employing various methods such as thematic analysis, content analysis, grounded theory, and narrative analysis. Through careful analysis and interpretation of qualitative data, researchers can derive valuable findings that contribute to a deeper understanding of human phenomena.
What are the 4 components of qualitative data analysis?
In qualitative data analysis, there are four key components that form the foundation of the analytical process. These components include data collection, data organisation, data interpretation, and drawing conclusions. Data collection involves gathering relevant information through methods such as interviews, observations, or document analysis. Once the data is collected, it needs to be organised systematically to identify patterns and themes. The next step is data interpretation, where researchers analyse the data to uncover underlying meanings and relationships. Finally, drawing conclusions involves synthesising the findings to formulate insightful interpretations and implications based on the analysed qualitative data. These four components work together cohesively to ensure a thorough and rigorous analysis of qualitative data in research studies.
What is the data analysis of qualitative research?
The data analysis of qualitative research involves the systematic examination and interpretation of non-numerical data collected through methods such as interviews, observations, and open-ended surveys. This process aims to uncover patterns, themes, and relationships within the data to derive meaningful insights and draw conclusions. Qualitative data analysis requires researchers to categorise and code the information, identify recurring themes, and make connections between different elements of the data. By engaging in a rigorous analytical process, researchers can gain a deeper understanding of participants’ perspectives, behaviours, and experiences, ultimately contributing to the richness and depth of qualitative research findings.