Understanding Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are two of the most significant technological advancements of the 21st century. These technologies are transforming industries, enhancing efficiencies, and opening new avenues for innovation. But what exactly are AI and ML, and how do they impact our daily lives?
What is Artificial Intelligence?
Artificial Intelligence refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, especially computer systems. These processes include learning (acquiring information and rules for using it), reasoning (using rules to reach approximate or definite conclusions), and self-correction.
AI can be classified into two categories: Narrow AI and General AI. Narrow AI is designed to perform a narrow task, such as facial recognition or internet searches. In contrast, General AI refers to systems that possess the ability to perform any intellectual task that a human can do, although this remains largely theoretical at present.
What is Machine Learning?
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that focuses on the development of algorithms that allow computers to learn from and make predictions based on data. Rather than being explicitly programmed for specific tasks, ML systems use statistical techniques to improve their performance over time as they process more data.
This capability makes ML particularly valuable in areas where it is difficult or impractical for humans to write precise instructions for tasks. Examples include speech recognition, recommendation systems, and predictive analytics.
The Relationship Between AI and ML
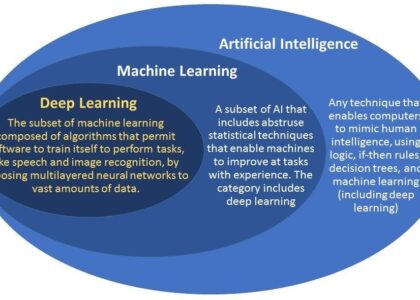
While often used interchangeably, AI and ML are distinct concepts. Machine Learning is a method used to achieve Artificial Intelligence. In other words, ML is one approach through which we can create intelligent behaviour in machines.
The relationship between the two can be thought of as hierarchical: all machine learning counts as artificial intelligence, but not all artificial intelligence uses machine learning.
Applications in Everyday Life
The impact of AI and ML can be seen across various sectors:
- Healthcare: AI-powered tools assist doctors in diagnosing diseases more accurately by analysing medical images.
- Finance: Machine learning algorithms detect fraudulent transactions by identifying unusual patterns in spending behaviour.
- E-commerce: Recommendation engines suggest products based on user preferences and past behaviour.
- Transportation: Autonomous vehicles use machine learning to navigate roads safely by processing real-time data from sensors.
The Future of AI and ML
The future holds immense potential for both AI and ML technologies. As these fields continue to evolve, they promise further advancements in automation, efficiency improvements across industries, enhanced decision-making capabilities through data analysis with artificial intelligence tools like ChatGPT-4 from OpenAI or Google’s BERT model among others – leading ultimately towards smarter societies globally!
A key challenge moving forward will be ensuring ethical considerations are addressed alongside technological progress so that benefits remain inclusive without compromising privacy rights or security concerns associated with widespread adoption worldwide! With careful management however there’s little doubt about transformative power held within reach thanks largely due ongoing research efforts driving us ever closer towards realising full potential offered up by these exciting domains today!
Unleashing the Potential: 7 Advantages of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning
- 1. Enhanced Efficiency
- 2. Improved Decision-Making
- 3. Personalisation
- 4. Predictive Analytics
- 5. Increased Productivity
- 6. Greater Accuracy
- 7. Innovation Opportunities
Challenges of Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning: Bias, Job Displacement, Privacy, Transparency, and Security Risks
1. Enhanced Efficiency
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning significantly enhance efficiency by automating repetitive tasks, thereby saving both time and resources. In various industries, AI-powered systems can handle routine operations such as data entry, scheduling, and customer service inquiries with remarkable speed and accuracy. This automation allows human workers to focus on more complex, value-added activities that require creativity and critical thinking. By reducing the burden of mundane tasks, organisations can optimise their workflows, increase productivity, and reduce operational costs. As a result, businesses are able to allocate their resources more effectively, driving innovation and growth while maintaining a competitive edge in the market.
2. Improved Decision-Making
Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning have revolutionised decision-making processes across various sectors by providing data-driven insights that enhance accuracy and efficiency. By analysing vast amounts of data quickly and accurately, AI systems can identify patterns and trends that might be overlooked by human analysis. This capability allows businesses to make more informed decisions, whether it’s optimising supply chains, predicting market trends, or tailoring customer experiences. In healthcare, for example, AI can assist doctors in diagnosing conditions by highlighting potential issues based on patient data. Consequently, AI-driven insights not only improve the quality of decisions but also enable quicker responses to changing conditions, ultimately leading to better outcomes across industries.
3. Personalisation
ML algorithms enable personalised user experiences in various applications. By analysing user data and behaviour patterns, artificial intelligence can tailor recommendations, content, and interactions to meet individual preferences and needs. This level of personalisation not only enhances user satisfaction but also increases engagement and loyalty towards the application or service. Whether it’s customised product recommendations on e-commerce platforms or personalised content suggestions on streaming services, AI-driven personalisation enriches the user experience by delivering relevant and valuable information tailored to each user’s unique interests and preferences.
4. Predictive Analytics
Predictive analytics, powered by artificial intelligence and machine learning, represents a significant advantage in today’s data-driven world. By analysing historical data, AI can forecast trends and predict outcomes with remarkable accuracy. This capability allows businesses to make informed decisions by anticipating future demands, identifying potential risks, and uncovering new opportunities. For instance, in retail, predictive analytics can optimise inventory management by forecasting sales patterns, while in finance, it can assess market trends to guide investment strategies. Ultimately, the ability of AI to provide actionable insights from past data empowers organisations to stay ahead of the curve and maintain a competitive edge.
5. Increased Productivity
Artificial intelligence and machine learning significantly enhance productivity by automating routine processes that would otherwise consume valuable time and resources. By taking over repetitive and mundane tasks, AI allows employees to focus on more complex and creative aspects of their work. This shift not only increases efficiency but also improves job satisfaction, as individuals can engage in activities that require critical thinking and innovation. Furthermore, automation through AI reduces the likelihood of human error in routine operations, ensuring higher accuracy and consistency in outcomes. Overall, the integration of AI into daily workflows leads to streamlined operations, enabling businesses to achieve more in less time while maintaining high standards of quality.
6. Greater Accuracy
One significant advantage of artificial intelligence and machine learning is the ability to achieve greater accuracy in complex calculations. Machine Learning models are designed to process vast amounts of data and identify patterns that may not be readily apparent to human analysts. By leveraging sophisticated algorithms, these models can deliver precise results consistently, leading to more reliable decision-making and outcomes across various industries and applications.
7. Innovation Opportunities
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are at the forefront of driving innovation across various sectors, unlocking unprecedented opportunities for technological advancements. By automating complex processes and analysing vast amounts of data with remarkable speed and accuracy, AI and ML enable businesses to explore new frontiers that were previously unimaginable. This technological prowess allows companies to develop cutting-edge products and services, optimise operations, and create personalised customer experiences. Furthermore, AI fosters a culture of innovation by encouraging experimentation and rapid prototyping, thus accelerating the pace at which new ideas are brought to market. As a result, industries ranging from healthcare to finance are witnessing transformative changes that not only enhance efficiency but also redefine the boundaries of what is achievable.
Bias in decision-making
One significant drawback of artificial intelligence and machine learning is the potential for bias in decision-making. AI and ML algorithms learn from the data they are trained on, which means that if this data contains biases, the algorithms can inadvertently perpetuate these biases. This can lead to unfair or discriminatory outcomes, particularly in sensitive areas such as hiring, lending, or law enforcement. For example, if historical data reflects societal prejudices, an AI system may make biased predictions or decisions that disproportionately affect certain groups. Addressing this issue requires careful attention to data selection and algorithm design to ensure fairness and equity in AI-driven processes.
Job displacement
The advent of artificial intelligence and machine learning has undoubtedly brought about significant advancements in various sectors, but it also poses the challenge of job displacement. As AI and ML technologies drive automation, many routine and manual tasks are becoming obsolete, leading to potential job losses across industries. Roles that involve repetitive or predictable activities are particularly at risk, as machines can perform these tasks more efficiently and cost-effectively than humans. This shift necessitates a re-evaluation of the workforce landscape, with an increasing emphasis on upskilling and reskilling to prepare workers for new opportunities in a technology-driven economy. While AI offers numerous benefits, addressing the social implications of job displacement remains crucial to ensure a balanced transition that supports both innovation and employment.
Privacy concerns
The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning into various applications often necessitates the collection and analysis of vast amounts of personal data, which raises significant privacy concerns. As these technologies become more pervasive, they gather detailed information about individuals’ behaviours, preferences, and interactions. This extensive data collection can lead to potential misuse if not properly managed and safeguarded. There is a risk that sensitive information could be accessed by unauthorised parties or used for purposes beyond the original intent, such as targeted advertising or surveillance. Ensuring robust data protection measures and transparent usage policies is crucial to mitigating these privacy issues and maintaining public trust in AI-driven systems.
Lack of transparency
One of the significant drawbacks of artificial intelligence and machine learning is the lack of transparency inherent in many complex algorithms. These systems often operate as “black boxes,” meaning that while they can process vast amounts of data and produce decisions or predictions, the inner workings behind these outcomes are not easily interpretable. This opacity can create challenges, especially in critical areas such as healthcare, finance, or legal systems, where understanding the rationale behind a decision is crucial. Without clear insights into how AI systems arrive at their conclusions, it becomes difficult to ensure accountability and trust. Moreover, this lack of transparency can hinder the identification and correction of biases within the algorithms, potentially leading to unfair or unethical outcomes. As AI continues to integrate into more aspects of daily life, addressing this issue becomes increasingly important to ensure responsible and equitable use of technology.
Security risks
One significant drawback of artificial intelligence and machine learning is the potential for security risks. AI systems, if not properly secured, can be vulnerable to various forms of attacks and manipulation. Cybercriminals may exploit these vulnerabilities to alter the behaviour of AI models, leading to incorrect outputs or even complete system failures. For instance, adversarial attacks can involve subtly modifying input data in a way that causes AI systems to make erroneous decisions. This poses substantial cybersecurity threats, particularly in critical sectors such as finance, healthcare, and transportation, where the integrity of AI systems is paramount. Ensuring robust security measures and continuous monitoring is essential to mitigate these risks and protect sensitive data from malicious actors.