Understanding Machine Learning in Artificial Intelligence
Machine learning is a pivotal subset of artificial intelligence (AI) that has gained significant attention in recent years. It involves the development of algorithms that enable computers to learn from and make decisions based on data. This transformative technology is reshaping industries and driving innovation across various sectors.
What is Machine Learning?
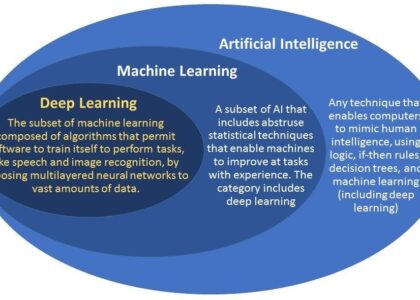
Machine learning is a branch of AI that focuses on building systems that can learn from data, identify patterns, and make decisions with minimal human intervention. Unlike traditional programming, where explicit instructions are provided, machine learning algorithms use statistical techniques to improve their performance as they process more data.
Types of Machine Learning
There are three main types of machine learning:
- Supervised Learning: In this approach, the algorithm is trained on a labelled dataset, meaning that each training example is paired with an output label. The model learns to predict the output from the input data.
- Unsupervised Learning: Here, the algorithm works with unlabelled data and tries to find hidden patterns or intrinsic structures within it. Clustering and association are common techniques used in unsupervised learning.
- Reinforcement Learning: This type involves training an agent to make sequences of decisions by rewarding desired behaviours and punishing undesired ones. It’s often used in robotics and game-playing AI.
The Role of Machine Learning in AI
Machine learning plays a crucial role in advancing AI technologies. It enables systems to perform complex tasks such as image recognition, natural language processing, and predictive analytics with high accuracy. By continuously learning from new data, machine learning models can adapt to changing environments and improve over time.
Applications of Machine Learning
The applications of machine learning are vast and varied:
- Healthcare: Machine learning algorithms assist in diagnosing diseases, personalising treatment plans, and predicting patient outcomes.
- Finance: Financial institutions use machine learning for fraud detection, risk management, and algorithmic trading.
- E-commerce: Recommendation systems powered by machine learning enhance customer experience by suggesting products based on user preferences.
- Agriculture: Precision farming utilises machine learning for crop monitoring, yield prediction, and resource optimisation.
The Future of Machine Learning
The future of machine learning holds immense potential as research continues to advance. Emerging areas such as deep learning—a subset focusing on neural networks—are pushing the boundaries of what machines can achieve. As computational power increases and more data becomes available, machine learning will continue to drive innovation across all sectors.
The integration of machine learning into everyday life promises not only efficiency but also the ability to solve complex problems previously thought insurmountable. As technology evolves, so too will the capabilities of artificial intelligence driven by robust machine-learning models.
This dynamic field continues to inspire researchers and developers around the world as they work towards creating intelligent systems capable of transforming how we live and work.
Understanding AI and Machine Learning: Key Questions Answered
- What is artificial intelligence in machine learning?
- What are the 4 types of AI?
- Is artificial intelligence the same as machine learning?
- What are the 4 types of ML?
- What are the 3 types of machine learning?
- Is machine learning the same as artificial intelligence?
- What is the salary of AI ML engineer?
- What is difference between AI and ML?
What is artificial intelligence in machine learning?
Artificial intelligence (AI) in the context of machine learning refers to the development of systems that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence by learning from data. Machine learning, a key component of AI, involves creating algorithms that enable computers to identify patterns and make decisions without explicit programming. Through exposure to vast amounts of data, these algorithms improve over time, allowing AI systems to perform complex functions such as image recognition, natural language processing, and predictive analytics. Essentially, machine learning provides the methodologies and tools through which AI systems can learn autonomously and adapt to new information or environments.
What are the 4 types of AI?
Artificial intelligence (AI) is typically categorised into four types, each representing a different level of capability and sophistication. The first type is Reactive Machines, which can only respond to specific inputs with predetermined outputs and lack memory or the ability to learn from past experiences. An example is IBM’s Deep Blue chess-playing computer. The second type is Limited Memory, which can retain data for a short period to inform decisions, such as self-driving cars that use historical data to make navigation choices. The third type is Theory of Mind, which refers to AI systems that can understand emotions, beliefs, and thoughts, allowing them to interact more naturally with humans; however, this type remains largely theoretical at present. The fourth and most advanced type is Self-Aware AI, which has its own consciousness and awareness; this stage remains speculative and has not yet been achieved in reality. These categories illustrate the progression from basic reactive systems to potentially autonomous entities capable of independent thought.
Is artificial intelligence the same as machine learning?
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning are closely related but distinct concepts. AI refers to the broader field of creating systems that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence, such as reasoning, problem-solving, and understanding language. Machine learning, on the other hand, is a subset of AI focused specifically on developing algorithms that allow computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed for each task. While all machine learning is a form of AI, not all AI relies solely on machine learning techniques. Other approaches within AI include rule-based systems and expert systems, which do not necessarily involve learning from data. Therefore, while they are interconnected, artificial intelligence encompasses a wider range of technologies beyond just machine learning.
What are the 4 types of ML?
In the realm of machine learning, there are four primary types of approaches: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, semi-supervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Supervised learning involves training a model on labelled data to predict outcomes. Unsupervised learning focuses on finding patterns in unlabelled data without specific output labels. Semi-supervised learning combines elements of both supervised and unsupervised learning by using a small amount of labelled data alongside unlabelled data. Reinforcement learning, on the other hand, involves training an agent to make sequences of decisions based on rewards and punishments to achieve a specific goal. Each type plays a distinct role in the field of machine learning, offering unique capabilities and applications in various domains.
What are the 3 types of machine learning?
Machine learning, a key component of artificial intelligence, is categorised into three primary types: supervised learning, unsupervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Supervised learning involves training a model on a labelled dataset, where the algorithm learns to map inputs to the correct outputs based on example input-output pairs. This type is commonly used in applications like image recognition and spam detection. Unsupervised learning, on the other hand, deals with unlabelled data and focuses on identifying hidden patterns or intrinsic structures within the data. Techniques such as clustering and association are typical in unsupervised learning scenarios, aiding in tasks like customer segmentation. Lastly, reinforcement learning involves an agent making decisions by interacting with an environment to achieve a goal. The agent learns by receiving rewards or penalties for its actions, which helps it develop strategies over time. This type of machine learning is often used in robotics and game playing, where decision-making processes are crucial.
Is machine learning the same as artificial intelligence?
Machine learning and artificial intelligence (AI) are closely related but distinct concepts. Artificial intelligence is a broad field that encompasses the creation of systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as understanding language, recognising patterns, and solving problems. Machine learning, on the other hand, is a subset of AI focused specifically on the development of algorithms that enable computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed for each task. While all machine learning is a form of AI, not all AI involves machine learning. Other areas within AI include rule-based systems and expert systems, which do not necessarily rely on data-driven learning processes. In essence, machine learning provides one of the key tools that drive advancements in artificial intelligence by allowing systems to adapt and evolve through experience.
What is the salary of AI ML engineer?
The salary of an AI/ML engineer can vary significantly depending on factors such as experience, location, industry, and company size. In general, AI/ML engineers are in high demand due to the increasing adoption of artificial intelligence technologies across various sectors. Salaries for AI/ML engineers tend to be competitive, with experienced professionals commanding higher pay scales. According to industry reports, the average salary for AI/ML engineers is often above the average for software engineers in other specialisations. It’s essential for individuals considering a career in AI/ML engineering to research current market trends and consult with industry professionals to gain a better understanding of salary expectations in this dynamic field.
What is difference between AI and ML?
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are closely related but distinct concepts in the realm of technology. AI refers to the broader field of creating machines or systems that can simulate human intelligence, encompassing a wide range of capabilities such as reasoning, problem-solving, and understanding language. It aims to create systems that can perform tasks typically requiring human intelligence. On the other hand, Machine Learning is a subset of AI focused specifically on the development of algorithms that allow computers to learn from data and improve their performance over time without being explicitly programmed for each task. While AI encompasses the overall goal of creating intelligent behaviour in machines, ML provides one of the primary methods by which this intelligence can be achieved, through pattern recognition and data-driven decision-making.