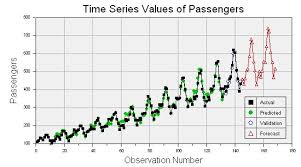
The Power of Time Series Analysis in Unveiling Insights
Time series analysis is a powerful statistical technique that allows us to extract valuable insights from sequential data points collected over time. It is widely used in various fields, including finance, economics, weather forecasting, and many more. By studying the patterns and trends within time series data, analysts can make informed decisions and predictions that drive strategic planning and decision-making.
Understanding Time Series Data
Time series data consists of observations recorded at regular intervals over a period of time. These data points are ordered chronologically and can exhibit patterns such as trends, seasonality, and cyclical variations. By analysing these patterns, analysts can uncover hidden relationships and dependencies within the data.
Applications of Time Series Analysis
Time series analysis plays a crucial role in various applications, such as:
- Financial Forecasting: Predicting stock prices, currency exchange rates, and market trends.
- Demand Forecasting: Estimating future demand for products or services based on historical sales data.
- Healthcare Analytics: Monitoring patient health metrics over time to predict disease progression or treatment outcomes.
- Climatology: Studying weather patterns and climate change by analysing historical meteorological data.
Techniques in Time Series Analysis
There are several techniques used in time series analysis to extract meaningful insights from the data:
- Trend Analysis: Identifying long-term trends or patterns in the data that indicate overall directionality.
- Seasonal Decomposition: Separating the time series into seasonal components to analyse recurring patterns.
- Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA): A popular model for forecasting future values based on past observations and trend information.
- Machine Learning Models: Using algorithms like LSTM (Long Short-Term Memory) networks for advanced time series prediction tasks.
The Future of Time Series Analysis
In an era where data is abundant and complex, the importance of time series analysis continues to grow. With advancements in machine learning and artificial intelligence, analysts now have more sophisticated tools at their disposal to uncover deeper insights from time-dependent datasets. As we move towards a more data-driven world, mastering the art of time series analysis will be key to unlocking valuable information that drives innovation and decision-making across industries.
In conclusion, time series analysis empowers us to understand the past, predict the future, and make informed decisions based on historical trends. By harnessing the power of sequential data analysis techniques, organisations can gain a competitive edge in today’s dynamic business landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions About Time Series Analysis: Key Steps, Components, and Examples
- What are the steps for time series analysis?
- What are the four main components of a time series?
- What is a time series example?
- What are the 4 components of time series analysis?
- What are the 4 components of time series?
What are the steps for time series analysis?
When embarking on time series analysis, it is essential to follow a structured approach to extract meaningful insights from the data. The steps for time series analysis typically involve data collection, data preprocessing (including handling missing values and outliers), identifying patterns and trends through visualisation, selecting an appropriate model (such as ARIMA or exponential smoothing), fitting the model to the data, validating the model’s performance using metrics like Mean Squared Error or AIC/BIC, and finally making forecasts or predictions based on the chosen model. Each step is crucial in understanding the underlying patterns within the time series data and leveraging them to make informed decisions or predictions.
What are the four main components of a time series?
In time series analysis, the four main components that define a time series data set are trend, seasonality, cyclicality, and irregularity. The trend component represents the long-term direction or pattern in the data, indicating whether values are increasing, decreasing, or remaining stable over time. Seasonality refers to recurring patterns or fluctuations that follow a specific time frame, such as daily, weekly, or monthly cycles. Cyclicality involves periodic variations that are not necessarily fixed to a specific time frame but repeat at irregular intervals. Irregularity represents random fluctuations or noise in the data that cannot be attributed to trend, seasonality, or cyclicality. Understanding and identifying these components are essential for accurate analysis and forecasting in time series data.
What is a time series example?
A time series example is a dataset that consists of observations recorded at regular intervals over a period of time. For instance, daily stock prices, monthly sales figures, hourly temperature readings, and annual GDP growth rates are all examples of time series data. By analysing these sequential data points, analysts can uncover trends, patterns, and relationships that provide valuable insights for forecasting future values or understanding underlying dynamics within the dataset. Time series examples are prevalent in various fields such as finance, economics, meteorology, and healthcare, highlighting the versatility and importance of this analytical technique in extracting meaningful information from temporal data.
What are the 4 components of time series analysis?
In time series analysis, there are four key components that help in understanding and interpreting the underlying patterns within sequential data. These components are trend, seasonality, cyclical variations, and irregular fluctuations. The trend component represents the long-term directionality or overall pattern in the data. Seasonality refers to recurring patterns that occur at regular intervals, such as daily, weekly, or monthly. Cyclical variations are fluctuations that do not have a fixed period and can extend beyond a year. Irregular fluctuations, also known as residual errors, capture random variations or unexpected events that cannot be attributed to the other components. By identifying and analysing these four components, analysts can gain valuable insights into the behaviour of time series data and make more accurate predictions and forecasts.
What are the 4 components of time series?
In time series analysis, the data is typically decomposed into four main components: trend, seasonality, cyclicality, and randomness. The trend component represents the long-term direction of the data, indicating whether it is increasing, decreasing, or stable over time. Seasonality refers to recurring patterns or fluctuations that follow a consistent periodicity within the data. Cyclicality captures repetitive but non-seasonal patterns that occur at irregular intervals. Lastly, randomness, also known as residual or error component, accounts for any unpredictable variability in the data that cannot be explained by the other components. Understanding and analysing these four components is essential for extracting meaningful insights and making accurate predictions using time series data.