The Power of Financial Data Analysis
Financial data analysis is a vital tool for businesses and individuals looking to make informed decisions about their finances. By examining and interpreting financial data, organisations can gain valuable insights into their performance, identify trends, and forecast future outcomes.
Benefits of Financial Data Analysis
Improved Decision-Making: By analysing financial data, businesses can make strategic decisions based on concrete evidence rather than intuition.
Risk Management: Financial data analysis helps in identifying potential risks and developing mitigation strategies to safeguard the financial health of an organisation.
Performance Evaluation: By comparing actual financial results with forecasts and benchmarks, companies can evaluate their performance and make necessary adjustments to achieve their goals.
Tools Used in Financial Data Analysis
In the digital age, various tools and technologies are employed for financial data analysis:
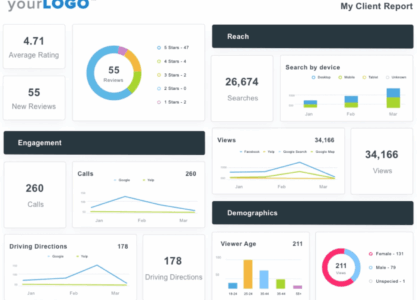
- Data Visualization Tools: Such as Tableau or Power BI, help in presenting complex financial data in a visually appealing format for better understanding.
- Statistical Software: Programs like R or Python are used for statistical analysis and modelling to uncover patterns in financial data.
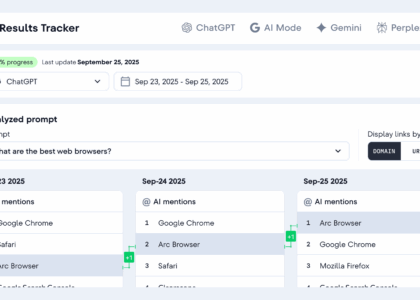
- Machine Learning Algorithms: AI-driven algorithms are utilised to predict future trends based on historical financial data.
The Future of Financial Data Analysis
The field of financial data analysis is continuously evolving with advancements in technology. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms is revolutionising how businesses analyse and utilise their financial data. As the volume and complexity of financial information grow, the need for sophisticated analytical tools will only increase.
In conclusion, financial data analysis is a powerful tool that empowers organisations to make informed decisions, manage risks effectively, and drive business growth. By harnessing the insights derived from analysing their financial data, businesses can stay competitive in an ever-changing market landscape.
Understanding Financial Data Analysis: Roles, Components, and Types Explained
- What does a financial data analyst do?
- What are the 5 components of financial analysis?
- What are the 3 types of financial analysis?
- What are the three types of financial analysis?
- What is a data analysis in finance?
What does a financial data analyst do?
A financial data analyst plays a crucial role in examining and interpreting financial data to provide valuable insights to businesses and organisations. These professionals are responsible for collecting, organising, and analysing financial information to identify trends, patterns, and opportunities that can influence strategic decision-making. By utilising various statistical tools, software, and techniques, a financial data analyst helps in forecasting future outcomes, evaluating performance metrics, and assessing risks. Their expertise in data analysis enables them to communicate complex findings in a clear and concise manner, assisting stakeholders in making informed financial decisions that drive business success.
What are the 5 components of financial analysis?
Financial analysis comprises five key components that are essential for evaluating the financial health and performance of an organisation. These components include profitability analysis, liquidity analysis, solvency analysis, efficiency analysis, and market valuation analysis. Profitability analysis focuses on assessing the company’s ability to generate profits and its overall financial performance. Liquidity analysis examines the organisation’s ability to meet short-term obligations. Solvency analysis evaluates the company’s long-term financial stability and ability to repay debts. Efficiency analysis assesses how effectively the company utilises its assets and resources. Market valuation analysis looks at the company’s market value compared to its financial metrics. By analysing these components comprehensively, stakeholders can gain a holistic understanding of a company’s financial position and make informed decisions.
What are the 3 types of financial analysis?
Financial analysis encompasses various types of analysis that provide insights into the financial health and performance of an organisation. The three main types of financial analysis are:
**Horizontal Analysis**: This type of analysis involves comparing financial data over a period to identify trends and changes in performance, such as year-on-year revenue growth or expense fluctuations.
**Vertical Analysis**: Vertical analysis focuses on the proportions of different items within a single period’s financial statements, helping to assess the relative significance of each item in relation to others.
3. **Ratio Analysis**: Ratio analysis involves calculating and interpreting key financial ratios to evaluate aspects such as liquidity, profitability, efficiency, and solvency, providing a comprehensive view of an entity’s financial position. Each type of financial analysis plays a crucial role in helping stakeholders make informed decisions and understand the overall financial picture of a business.
What are the three types of financial analysis?
Financial analysis encompasses three main types: 1) Horizontal analysis, which involves comparing financial data over a period to identify trends and changes in performance; 2) Vertical analysis, where financial data is presented as a percentage of a base figure to assess the relative proportions of different components within a single period; and 3) Ratio analysis, which involves evaluating relationships between different financial variables to gauge the financial health and performance of an organisation. Each type of financial analysis provides valuable insights into the financial standing and operational efficiency of a business, aiding stakeholders in making well-informed decisions.
What is a data analysis in finance?
In the realm of finance, data analysis refers to the process of examining and interpreting financial information to extract meaningful insights and make informed decisions. It involves scrutinising vast amounts of financial data, such as income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and market trends, to identify patterns, trends, and relationships. By employing statistical techniques, modelling tools, and software applications, data analysis in finance helps businesses evaluate their performance, assess risks, forecast future outcomes, and ultimately enhance their financial strategies. This analytical approach enables organisations to gain a deeper understanding of their financial position and make strategic decisions based on empirical evidence rather than conjecture.