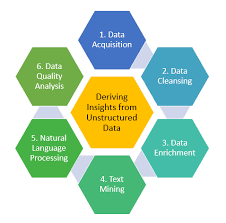
The Power of Unstructured Data Analytics
In today’s digital age, the amount of data generated is staggering. From social media posts and emails to images and videos, a significant portion of this data is unstructured – meaning it doesn’t fit neatly into traditional databases or spreadsheets. Harnessing the power of unstructured data through analytics has become increasingly crucial for businesses looking to gain valuable insights and stay competitive in their respective industries.
What is Unstructured Data?
Unstructured data refers to information that doesn’t have a predefined data model or is not organized in a structured manner. This type of data can come in various forms, including text files, multimedia content, social media posts, sensor data, and more. Unlike structured data found in databases with defined fields and tables, unstructured data presents unique challenges due to its complexity and lack of uniformity.
The Challenges of Unstructured Data
Analysing unstructured data poses several challenges for businesses. Traditional methods of data analysis may not be suitable for extracting meaningful insights from this type of data due to its diverse formats and varying quality. Additionally, unstructured data often contains valuable but hidden information that can be difficult to uncover without advanced analytics tools.
The Benefits of Unstructured Data Analytics
By leveraging advanced analytics techniques such as natural language processing (NLP), machine learning, and artificial intelligence (AI), businesses can unlock the potential of unstructured data. These tools enable organisations to extract valuable insights from text documents, images, videos, and audio files that were previously untapped.
Applications of Unstructured Data Analytics
Unstructured data analytics has a wide range of applications across industries. For example:
- Marketing: Analysing social media posts and customer reviews to understand sentiment and improve marketing strategies.
- Healthcare: Extracting insights from medical records and clinical notes to enhance patient care and treatment outcomes.
- Retail: Analysing customer feedback and product reviews to identify trends and improve product offerings.
- Finance: Analysing news articles and market reports to make informed investment decisions.
The Future of Unstructured Data Analytics
As the volume of unstructured data continues to grow exponentially, the importance of leveraging advanced analytics tools will only increase. Businesses that embrace unstructured data analytics will have a competitive edge by gaining deeper insights into customer behaviour, market trends, and operational efficiency.
Unlocking the Potential of Unstructured Data: 7 Key Advantages for Business Success
- 1. Gain valuable insights from diverse data sources.
- 2. Identify emerging trends and patterns hidden in unstructured data.
- 3. Enhance decision-making with more comprehensive and accurate information.
- 4. Improve customer satisfaction by understanding sentiment from unstructured text data.
- 5. Boost operational efficiency through better analysis of multimedia content.
- 6. Drive innovation by leveraging advanced analytics techniques on unstructured data.
- 7. Stay ahead of competitors by harnessing the power of untapped data sources.
Challenges in Unstructured Data Analytics: Navigating Complexity, Quality, Privacy, and More
- Complexity
- Quality Issues
- Data Privacy Concerns
- Scalability Challenges
- Costly Infrastructure
- Lack of Standardisation
- Interpretation Complexity
1. Gain valuable insights from diverse data sources.
Unstructured data analytics offers the significant advantage of enabling businesses to gain valuable insights from diverse data sources. By analysing unstructured data such as text documents, social media posts, images, and videos, organisations can extract meaningful information that may not be accessible through traditional structured data analysis methods. This allows businesses to uncover hidden patterns, trends, and relationships across a wide range of sources, providing a more comprehensive understanding of their operations, customers, and market landscape.
2. Identify emerging trends and patterns hidden in unstructured data.
Unstructured data analytics offers the valuable advantage of uncovering emerging trends and patterns that may be hidden within vast amounts of unstructured data. By utilising advanced analytics techniques such as natural language processing and machine learning, businesses can extract meaningful insights from sources like social media posts, customer feedback, and online content. This capability enables organisations to identify trends early on, understand consumer preferences, and make informed strategic decisions based on real-time data analysis. The ability to spot hidden patterns in unstructured data empowers businesses to stay ahead of the curve and adapt quickly to changing market dynamics.
3. Enhance decision-making with more comprehensive and accurate information.
Unstructured data analytics offers the significant advantage of enhancing decision-making by providing organisations with more comprehensive and accurate information. By analysing diverse sources of unstructured data such as social media posts, customer feedback, and multimedia content, businesses can gain deeper insights into consumer preferences, market trends, and operational performance. This wealth of information enables decision-makers to make informed choices based on a holistic view of the data landscape, leading to more effective strategies and better outcomes for the organisation.
4. Improve customer satisfaction by understanding sentiment from unstructured text data.
One significant advantage of unstructured data analytics is the ability to enhance customer satisfaction by gaining insights into sentiment from unstructured text data. By analysing customer feedback, social media posts, and reviews using advanced analytics tools such as natural language processing (NLP), businesses can better understand the emotions and opinions expressed by their customers. This deeper understanding allows companies to identify areas for improvement, address concerns proactively, and tailor their products or services to meet customer preferences effectively, ultimately leading to increased customer satisfaction and loyalty.
5. Boost operational efficiency through better analysis of multimedia content.
Unstructured data analytics offers the significant advantage of boosting operational efficiency through improved analysis of multimedia content. By utilising advanced analytics techniques such as image and video recognition, businesses can extract valuable insights from multimedia sources that were previously challenging to interpret. This enhanced analysis allows organisations to streamline processes, make informed decisions, and identify opportunities for improvement, ultimately leading to increased operational efficiency and productivity across various sectors.
6. Drive innovation by leveraging advanced analytics techniques on unstructured data.
By harnessing advanced analytics techniques on unstructured data, businesses can drive innovation to new heights. The ability to extract valuable insights from diverse sources such as text documents, images, and multimedia content allows companies to uncover hidden patterns, trends, and opportunities that traditional data analysis methods might overlook. By delving deep into unstructured data with tools like natural language processing and machine learning, organisations can uncover innovative solutions, create unique products and services, and stay ahead of the curve in a rapidly evolving market landscape.
7. Stay ahead of competitors by harnessing the power of untapped data sources.
By harnessing the power of unstructured data analytics, businesses can stay ahead of competitors by tapping into previously untapped data sources. This enables organisations to extract valuable insights from diverse sources such as social media posts, customer feedback, and multimedia content, giving them a competitive edge in understanding market trends, customer preferences, and emerging opportunities. By unlocking the potential of unstructured data, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of their operations and make informed decisions that drive innovation and growth, setting them apart from their rivals in today’s fast-paced digital landscape.
Complexity
One significant drawback of unstructured data analytics is the inherent complexity it presents. Analysing unstructured data demands advanced tools and expertise to navigate the diverse range of data formats effectively. Unlike structured data that follows a predefined model, unstructured data requires sophisticated techniques such as natural language processing and machine learning to extract valuable insights. This complexity can pose challenges for businesses without the necessary resources or expertise, making it difficult to harness the full potential of unstructured data for informed decision-making and strategic planning.
Quality Issues
Quality is a significant concern when dealing with unstructured data analytics. The inherent lack of structure in this type of data can lead to inconsistencies, errors, and irrelevant information being present. These quality issues can significantly impact the accuracy and reliability of the analysis conducted on unstructured data. Without proper measures in place to address and mitigate these challenges, businesses risk drawing incorrect conclusions or making decisions based on flawed insights derived from unstructured data.
Data Privacy Concerns
Analysing unstructured data raises significant data privacy concerns, particularly due to the potential presence of sensitive or personally identifiable information within the data. As businesses delve into unstructured data to extract insights, there is a risk of inadvertently accessing and processing personal data without proper consent or safeguards in place. This poses a challenge in ensuring compliance with data protection regulations and maintaining the trust of individuals whose information may be included in the analysis. Data privacy considerations must be carefully addressed when conducting unstructured data analytics to mitigate the risks associated with handling confidential or private information.
Scalability Challenges
Scalability challenges present a significant con when it comes to unstructured data analytics. As the volume of data continues to grow exponentially over time, scaling up the analytics processes to handle this increasing load can be a daunting task. The infrastructure and resources required to effectively process and analyse large amounts of unstructured data may need constant adjustments and upgrades to keep up with the expanding data sets. Failure to address scalability challenges can lead to performance issues, delays in insights generation, and potential bottlenecks in the analytics workflow.
Costly Infrastructure
One significant drawback of unstructured data analytics is the costly infrastructure required for its implementation and maintenance. Businesses face substantial expenses in setting up the necessary hardware, software, and storage systems to effectively analyse unstructured data. Additionally, ongoing maintenance costs can quickly add up, especially when considering the need for regular updates and upgrades to keep pace with evolving technologies. The financial investment needed to support unstructured data analytics can be a barrier for many organisations looking to leverage the potential insights hidden within their data.
Lack of Standardisation
One significant drawback of unstructured data analytics is the lack of standardisation. Unstructured data, by its nature, does not adhere to a uniform format or structure, making it challenging to establish consistent analysis processes across various types of data sources. This lack of standardisation can lead to difficulties in integrating and interpreting data effectively, potentially resulting in inconsistencies and inaccuracies in the analytical outcomes. Addressing this con requires careful consideration and implementation of robust data management strategies to ensure reliable and meaningful insights are derived from unstructured data sources.
Interpretation Complexity
Interpretation Complexity is a significant con of unstructured data analytics. Extracting valuable insights from unstructured data often demands advanced interpretation techniques, such as natural language processing and machine learning algorithms. These methods can be intricate and time-consuming, requiring skilled data analysts to navigate through the complexity of diverse data formats and extract meaningful information. The need for sophisticated interpretation adds a layer of challenge to the analysis process, potentially slowing down decision-making and hindering the timely extraction of insights from unstructured data sources.