Understanding the Evolution of Artificial Intelligence: Machine Learning and Deep Learning
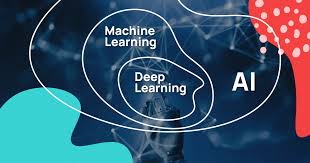
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has become a cornerstone of modern technology, driving advancements across numerous industries. Within the realm of AI, two significant subfields have emerged: Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL). These technologies have revolutionised how machines process data and make decisions, leading to more intelligent and autonomous systems.
What is Machine Learning?
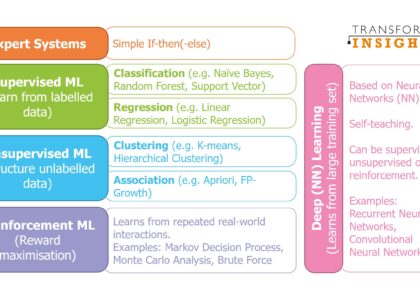
Machine Learning is a subset of AI that focuses on developing algorithms that allow computers to learn from and make predictions based on data. Rather than being explicitly programmed to perform a task, ML systems use statistical techniques to improve their performance as they are exposed to more data over time.
The core idea behind ML is to enable machines to learn patterns and relationships in data, allowing them to make informed decisions without human intervention. This capability has been applied in various fields such as finance for fraud detection, healthcare for predictive diagnostics, and retail for personalised recommendations.
The Emergence of Deep Learning
Deep Learning is a specialised branch of Machine Learning that utilises neural networks with many layers—hence the term “deep.” These deep neural networks are designed to mimic the human brain’s structure and function, enabling machines to process complex patterns in large datasets.
The rise of Deep Learning has been largely driven by advancements in computational power and the availability of vast amounts of data. This approach has proven particularly successful in areas such as image recognition, natural language processing (NLP), and autonomous vehicles.
Key Differences Between Machine Learning and Deep Learning
- Data Dependency: While traditional ML algorithms can work effectively with smaller datasets, DL models typically require large volumes of data to achieve high performance due to their complexity.
- Feature Engineering: In ML, feature engineering—manually selecting relevant features—is often necessary. In contrast, DL models automatically discover features through their layered architecture.
- Computational Power: DL requires significantly more computational resources than ML due to its intricate network structures and extensive training processes.
The Impact on Industry
The integration of Machine Learning and Deep Learning into industry processes has led to significant improvements in efficiency, accuracy, and innovation. For instance:
- Healthcare: AI-driven diagnostics can analyse medical images faster than humans while maintaining high accuracy levels.
- Finance: Predictive analytics powered by ML helps financial institutions manage risks better by identifying potential fraud cases early on.
- E-commerce: Personalised shopping experiences are enhanced through recommendation engines that leverage user behaviour data using DL techniques.
The Future of AI: A Combined Approach
The future landscape of AI will likely see an increasing convergence between Machine Learning and Deep Learning methodologies. As these technologies continue evolving alongside advancements in hardware capabilities like quantum computing or edge devices’ proliferation—AI systems will become even more sophisticated at tackling complex real-world problems efficiently across diverse domains worldwide.
This evolution promises exciting opportunities for businesses seeking competitive advantages through intelligent automation solutions powered by cutting-edge artificial intelligence technologies such as machine learning & deep learning combined effectively together under one unified framework!
7 Essential Tips for Navigating Machine Learning, AI, and Deep Learning
Machine Learning
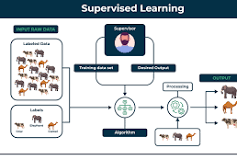
Machine Learning is a powerful subset of Artificial Intelligence that empowers machines to learn from data and improve their performance over time without explicit programming. By identifying patterns and relationships within datasets, Machine Learning algorithms can make informed decisions and predictions, revolutionising industries such as healthcare, finance, and retail. Its adaptive nature and ability to handle vast amounts of data make Machine Learning a cornerstone of modern technological advancements, paving the way for more intelligent and efficient systems.
AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) serves as the overarching concept that encompasses both Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL), driving innovation across various sectors. AI refers to the simulation of human intelligence processes by machines, particularly computer systems. These processes include learning, reasoning, and self-correction. While traditional AI systems relied heavily on predefined rules and logic, the advent of ML and DL has shifted the focus towards data-driven approaches. ML enables systems to learn from data patterns, improving over time without explicit programming. DL takes this a step further by employing neural networks with multiple layers to process vast amounts of data and extract intricate patterns. Together, these technologies allow AI to tackle complex tasks such as natural language processing, image recognition, and decision-making with unprecedented accuracy and efficiency. As AI continues to evolve, its integration into everyday applications promises to transform industries by enhancing productivity and enabling new capabilities.
Deep Learning
Deep Learning, a subset of Artificial Intelligence (AI) that utilises neural networks with multiple layers, has revolutionised the field of machine learning. By mimicking the structure and function of the human brain, deep learning algorithms can process complex patterns in vast datasets, leading to remarkable advancements in areas such as image recognition, natural language processing, and autonomous systems. The depth and complexity of deep learning models enable machines to learn intricate features directly from data, making them incredibly powerful tools for solving challenging problems across various industries.
To effectively harness the power of machine learning and deep learning, it’s crucial to focus on data quality rather than just quantity. High-quality data can significantly enhance the performance of models, leading to more accurate predictions and insights. This involves ensuring that the data is clean, well-organised, and relevant to the specific problem being addressed. Additionally, understanding the context and nuances of the data can help in selecting appropriate features and algorithms. By prioritising quality over sheer volume, businesses can develop AI solutions that are not only efficient but also robust and reliable in real-world applications.
Machine Learning
Machine Learning is a fundamental concept within the realm of artificial intelligence that empowers machines to learn from data and improve their performance over time without explicit programming. By identifying patterns and relationships in datasets, Machine Learning algorithms enable systems to make informed decisions autonomously. This transformative technology has revolutionised various industries by enhancing efficiency, accuracy, and innovation through predictive analytics, personalised recommendations, and automated decision-making processes.
AI
Artificial Intelligence (AI) serves as the overarching framework that encompasses both Machine Learning and Deep Learning, acting as the driving force behind these transformative technologies. AI focuses on creating systems capable of performing tasks that typically require human intelligence, such as understanding natural language, recognising patterns, and making decisions. Within this broad field, Machine Learning provides the tools for systems to learn from data and improve over time without being explicitly programmed. Deep Learning takes this a step further by employing neural networks to simulate human brain activity, allowing for more complex data analysis and decision-making processes. Together, these technologies are revolutionising industries by automating tasks, enhancing efficiency, and providing insights that were previously unattainable. As AI continues to evolve, its integration with Machine Learning and Deep Learning will undoubtedly lead to even more sophisticated applications across various sectors.
Deep Learning
Deep Learning is a powerful subset of artificial intelligence that involves the use of deep neural networks to process complex patterns and data. By mimicking the structure and function of the human brain, Deep Learning algorithms can autonomously learn from vast amounts of data to make accurate predictions and decisions. This technology has revolutionised various industries, such as healthcare, finance, and autonomous driving, by enabling machines to understand and interpret data in a more sophisticated manner than traditional machine learning approaches.