Understanding Deep Learning AI: Revolutionising Technology
Deep learning, a subset of artificial intelligence (AI), is transforming the technological landscape with its ability to mimic the human brain’s neural networks. This advanced form of machine learning has become integral to various applications, from voice assistants to autonomous vehicles. In this article, we explore what deep learning is, how it works, and its impact on different industries.
What is Deep Learning?
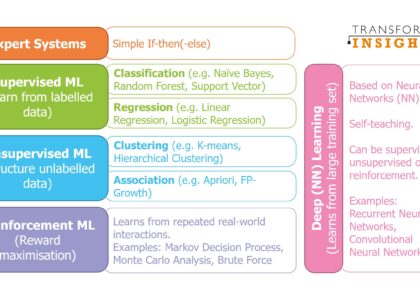
Deep learning involves training artificial neural networks with multiple layers to learn and make decisions on their own. Unlike traditional machine learning algorithms that require structured data inputs, deep learning models can process unstructured data such as images, text, and audio. This capability allows them to recognise patterns and make predictions with remarkable accuracy.
How Does Deep Learning Work?
The core component of deep learning is the neural network, which consists of interconnected nodes or neurons arranged in layers. Each layer processes input data and passes it through an activation function before sending it to the next layer. The network adjusts itself through a process called backpropagation, where errors are calculated and weights are updated to improve accuracy over time.
This iterative process enables deep learning models to improve their performance as they are exposed to more data. The depth of the network—referring to the number of layers—allows for complex representations and high-level abstractions of data.
Applications Across Industries
Deep learning AI has found applications across numerous sectors:
- Healthcare: From diagnosing diseases through medical imaging to personalising treatment plans, deep learning is revolutionising patient care.
- Automotive: Autonomous vehicles rely heavily on deep learning for tasks such as object detection and decision-making in real-time environments.
- Finance: Fraud detection systems use deep learning algorithms to analyse transaction patterns and identify anomalies.
- E-commerce: Recommendation engines powered by deep learning enhance customer experience by predicting user preferences based on past behaviour.
- Agriculture: Deep learning aids in crop monitoring and yield prediction by analysing satellite imagery and environmental data.
The Future of Deep Learning
The potential of deep learning continues to grow as researchers develop more sophisticated models and techniques. However, challenges remain, such as the need for large datasets and significant computational resources. Despite these hurdles, advancements in hardware technology and innovative approaches like transfer learning are expected to drive further progress.
The future promises even greater integration of deep learning into everyday life, making technology smarter and more intuitive than ever before.
Conclusion
Deep learning AI represents a significant leap forward in technology’s ability to understand and interact with the world around us. As its applications expand across various domains, it will continue reshaping industries and enhancing our capabilities in ways previously thought impossible. Embracing this technology will undoubtedly lead us towards a more intelligent future.
Exploring Deep Learning AI: Key Questions and Insights for Understanding Its Impact and Challenges
- What is deep learning AI?
- How does deep learning differ from traditional machine learning?
- What are the applications of deep learning in real-world scenarios?
- What are the key components of a deep learning neural network?
- How does backpropagation work in deep learning models?
- What challenges are associated with training deep learning algorithms?
- How can businesses leverage deep learning for competitive advantage?
- What role does data quality play in the effectiveness of deep learning models?
- What ethical considerations surround the use of deep learning AI?
What is deep learning AI?
Deep learning AI is a specialised branch of artificial intelligence that focuses on mimicking the human brain’s neural networks to process data and create patterns for decision-making. It involves the use of artificial neural networks with multiple layers—often referred to as deep neural networks—that enable machines to learn from vast amounts of unstructured data such as images, text, and audio. Unlike traditional machine learning, which often requires manual feature extraction, deep learning models automatically discover intricate structures within the data. This capability allows them to achieve remarkable accuracy in tasks like image recognition, natural language processing, and speech recognition. By continuously refining their performance through a process called backpropagation, deep learning systems become increasingly adept at making predictions and recognising patterns over time.
How does deep learning differ from traditional machine learning?
Deep learning differs from traditional machine learning in its approach to processing and understanding data. While traditional machine learning algorithms require manual feature extraction and selection by humans, deep learning models can automatically learn hierarchical representations of data through multiple layers of neural networks. This allows deep learning to handle unstructured data such as images, text, and audio more effectively, without the need for explicit feature engineering. The depth and complexity of neural networks in deep learning enable them to capture intricate patterns and relationships in the data, leading to higher accuracy and performance in tasks such as image recognition, natural language processing, and speech recognition.
What are the applications of deep learning in real-world scenarios?
Deep learning, a powerful subset of artificial intelligence, is increasingly being applied across various real-world scenarios, revolutionising industries with its advanced capabilities. In healthcare, deep learning algorithms are utilised for diagnosing diseases through medical imaging analysis and predicting patient outcomes. The automotive industry benefits from deep learning in the development of autonomous vehicles, where it aids in real-time object detection and navigation. In finance, deep learning models enhance fraud detection systems by analysing transaction patterns to identify anomalies swiftly. E-commerce platforms use deep learning to power recommendation engines that personalise shopping experiences by predicting customer preferences. Additionally, in agriculture, deep learning assists in monitoring crop health and optimising yields through the analysis of satellite imagery and environmental data. These applications demonstrate how deep learning is transforming traditional processes and driving innovation across multiple sectors.
What are the key components of a deep learning neural network?
In deep learning neural networks, the key components include layers of interconnected nodes, known as neurons, organised in a hierarchical structure. These layers typically consist of an input layer, one or more hidden layers, and an output layer. Each neuron receives input data, processes it using activation functions, and passes the transformed information to the next layer. The neural network learns by adjusting the weights of connections between neurons through backpropagation, a process that helps improve the model’s accuracy over time. The depth of the network, determined by the number of hidden layers, enables complex feature extraction and abstraction of data for making accurate predictions and classifications.
How does backpropagation work in deep learning models?
In deep learning models, backpropagation is a fundamental process that enables neural networks to learn from data and improve their performance over time. Essentially, backpropagation works by calculating the gradient of the loss function with respect to the model’s parameters. This gradient indicates how much each parameter contributes to the error in the model’s predictions. By propagating this gradient backwards through the network, from the output layer to the input layer, the model can adjust its weights and biases accordingly to minimise the error. Through iterative updates based on backpropagation, deep learning models can fine-tune their parameters and enhance their ability to make accurate predictions.
What challenges are associated with training deep learning algorithms?
Training deep learning algorithms poses several challenges that researchers and practitioners often encounter. One major challenge is the requirement for vast amounts of labelled data to effectively train these models. Obtaining high-quality, annotated datasets can be time-consuming and expensive, limiting the scalability of deep learning applications. Additionally, deep learning algorithms are computationally intensive and demand significant processing power, often necessitating access to specialised hardware such as GPUs. Another common challenge is the potential for overfitting, where the model performs well on training data but fails to generalise to unseen examples. Addressing these challenges requires a combination of domain expertise, computational resources, and innovative techniques to ensure the successful training of robust deep learning algorithms.
How can businesses leverage deep learning for competitive advantage?
Businesses can leverage deep learning for a competitive advantage by harnessing its power to extract valuable insights from vast amounts of data. Deep learning algorithms can analyse complex patterns, trends, and correlations within the data, providing businesses with actionable intelligence to make informed decisions. By implementing deep learning solutions in areas such as customer segmentation, predictive analytics, and process automation, companies can enhance operational efficiency, improve customer satisfaction, and drive innovation. Ultimately, leveraging deep learning allows businesses to stay ahead of the competition by unlocking new opportunities and gaining a deeper understanding of their markets and customers.
What role does data quality play in the effectiveness of deep learning models?
The quality of data plays a critical role in determining the effectiveness of deep learning models. In deep learning AI, the model learns patterns and makes predictions based on the data it is trained on. Therefore, if the input data is inaccurate, incomplete, or biased, it can lead to erroneous conclusions and hinder the model’s performance. High-quality data ensures that the model can learn meaningful representations and make reliable decisions. Data preprocessing steps such as cleaning, normalising, and augmenting are essential to improve data quality and enhance the overall accuracy and generalisation capabilities of deep learning models.
What ethical considerations surround the use of deep learning AI?
The use of deep learning AI brings several ethical considerations to the forefront, primarily concerning privacy, bias, and accountability. As these systems often require vast amounts of data to function effectively, there is a significant risk of infringing on individual privacy rights if data is not collected and handled responsibly. Additionally, deep learning models can inadvertently perpetuate or even exacerbate existing biases present in their training data, leading to unfair or discriminatory outcomes. This raises concerns about fairness and equality in decision-making processes that rely on AI. Moreover, the complexity and opacity of deep learning systems make it challenging to attribute accountability when errors occur or when AI-driven decisions have adverse impacts. Ensuring transparency and establishing clear guidelines for the ethical deployment of deep learning AI are crucial steps in addressing these challenges.