Understanding Supervised Learning in Artificial Intelligence
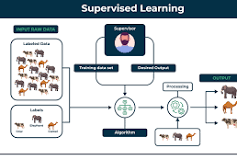
Supervised learning is a fundamental concept in the field of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. It involves training a model on a labelled dataset, meaning that each training example is paired with an output label. This approach allows the model to learn the relationship between input data and the corresponding output, enabling it to make predictions on new, unseen data.
The Basics of Supervised Learning
In supervised learning, the goal is to map input variables (features) to an output variable (label) based on example input-output pairs. The process involves two main phases: training and testing.
- Training Phase: During this phase, a machine learning algorithm is fed with a large amount of labelled data. The algorithm analyses this data and learns patterns or relationships between the features and the labels.
- Testing Phase: Once trained, the model is tested with new data that it hasn’t seen before. The purpose of this phase is to evaluate how well the model has learned from the training data by measuring its accuracy in predicting labels for new inputs.
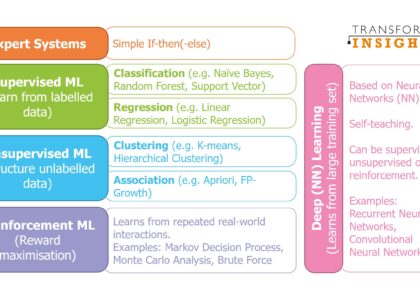
Types of Supervised Learning Algorithms
There are several types of algorithms used in supervised learning, each suited for different types of tasks:
- Regression Algorithms: These are used when the output variable is continuous. Examples include linear regression, polynomial regression, and support vector regression.
- Classification Algorithms: These are used when the output variable is categorical. Examples include logistic regression, decision trees, random forests, and support vector machines.
Applications of Supervised Learning
The applications of supervised learning are vast and varied across different industries:
- Email Filtering: Classifying emails as spam or not spam based on their content.
- Medical Diagnosis: Predicting diseases based on patient health records and symptoms.
- Securities Trading: Predicting stock prices using historical trading data.
- NLP Tasks: Language translation and sentiment analysis using text classification techniques.
The Importance of Quality Data
The success of a supervised learning model heavily depends on the quality and quantity of labelled data available for training. High-quality datasets ensure that the model learns accurate patterns without being biased or overfitting to noise within the dataset.
Challenges in Supervised Learning
A few challenges that practitioners face in supervised learning include dealing with large datasets that require significant computational resources, addressing class imbalance where certain categories dominate others within a dataset, and ensuring generalisation so that models perform well on unseen data rather than just memorising training examples.
The Future of Supervised Learning
The field continues to evolve rapidly with advancements in algorithms improving accuracy while reducing computational requirements. Moreover, combining supervised learning with other AI methodologies like unsupervised or reinforcement learning holds promise for even more sophisticated applications across various domains in future developments within artificial intelligence technology landscapes globally today!
The continued research into developing robust models capable enough not only predicting accurately but also explaining decisions made by these systems remains crucial towards fostering trustworthiness among users relying upon insights derived through such technological innovations worldwide tomorrow!
Advantages of Supervised Learning in AI: Precision, Versatility, and Adaptability
- Supervised learning enables accurate predictions by learning from labelled data.
- It is widely used in various industries for tasks like classification and regression.
- The process of supervised learning is relatively easy to understand and implement.
- Models trained through supervised learning can be easily evaluated for performance.
- It helps in automating decision-making processes based on historical data patterns.
- Supervised learning algorithms can handle both numerical and categorical data effectively.
- By continuously training with new data, supervised models can adapt to changing trends.
Challenges of Supervised Learning in AI: Data Dependency, Overfitting, and Ethical Concerns
- Dependence on labelled data for training, which can be time-consuming and costly to acquire.
- Difficulty in handling unbalanced datasets where certain classes are underrepresented.
- Risk of overfitting to the training data, leading to poor generalisation on unseen data.
- Vulnerability to noise and outliers in the training dataset, impacting model performance.
- Limited interpretability of complex models, making it challenging to understand how predictions are made.
- Ethical concerns related to biased or discriminatory outcomes if the training data is not representative or contains inherent biases.
Supervised learning enables accurate predictions by learning from labelled data.
One significant advantage of supervised learning in artificial intelligence is its ability to make precise predictions through the process of learning from labelled data. By training a model on a dataset where each input is associated with a known output, the algorithm can learn the underlying patterns and relationships within the data. This enables the model to generalise and make accurate predictions on new, unseen data based on the patterns it has learned during training. The use of labelled data allows supervised learning algorithms to understand complex relationships and make informed decisions, leading to reliable and precise outcomes in various applications across different industries.
It is widely used in various industries for tasks like classification and regression.
Supervised learning in artificial intelligence offers a significant advantage by being widely utilised across diverse industries for essential tasks such as classification and regression. In sectors ranging from healthcare and finance to marketing and technology, the ability of supervised learning algorithms to accurately classify data into categories or predict numerical values based on historical examples plays a crucial role in decision-making processes. By leveraging the power of labelled datasets, supervised learning empowers organisations to extract valuable insights, enhance operational efficiency, and drive innovation in their respective fields.
The process of supervised learning is relatively easy to understand and implement.
Supervised learning in artificial intelligence is often praised for its straightforward and intuitive nature, making it accessible to a wide range of practitioners, from beginners to experts. The process involves using labelled datasets, where each input is paired with a known output, allowing models to learn relationships between data points with relative ease. This clarity simplifies both the implementation and the interpretation of results, as users can easily trace how inputs are mapped to outputs. Additionally, the availability of numerous algorithms and tools designed specifically for supervised learning further streamlines the development process. As a result, individuals and organisations can quickly deploy effective AI solutions without needing an extensive background in complex mathematical theories or computational techniques.
Models trained through supervised learning can be easily evaluated for performance.
One of the significant advantages of supervised learning in artificial intelligence is that models trained through this approach can be easily evaluated for performance. Since supervised learning relies on labelled datasets, it provides a clear framework for assessing how well a model predicts the correct outputs. By comparing the predicted labels with the actual labels in a test dataset, practitioners can calculate various performance metrics such as accuracy, precision, recall, and F1 score. This straightforward evaluation process allows for quick identification of areas where the model excels or requires improvement. Consequently, it facilitates iterative refinement and optimisation of the model to enhance its predictive capabilities and ensure it meets the desired performance standards.
It helps in automating decision-making processes based on historical data patterns.
Supervised learning in artificial intelligence significantly enhances the automation of decision-making processes by leveraging historical data patterns. By training models on labelled datasets, businesses can automate complex decisions that would traditionally require human intervention. This capability allows organisations to swiftly and accurately respond to various scenarios based on learned patterns from past data. For instance, in financial services, supervised learning models can analyse historical transaction data to detect fraudulent activities in real-time, thereby reducing the need for manual oversight and enhancing security measures. This not only improves efficiency but also ensures consistency and reliability in decision-making across different sectors.
Supervised learning algorithms can handle both numerical and categorical data effectively.
One significant advantage of supervised learning algorithms in artificial intelligence is their ability to effectively handle both numerical and categorical data. Unlike some other machine learning approaches that struggle with mixed data types, supervised learning models can seamlessly process and derive meaningful insights from a combination of numerical values and categorical variables. This versatility enables the algorithms to tackle a wide range of real-world problems where data comes in various forms, making supervised learning a powerful tool for diverse applications across industries.
By continuously training with new data, supervised models can adapt to changing trends.
One significant advantage of supervised learning in artificial intelligence is its ability to adapt to changing trends by continuously training with new data. As the model receives updated information, it can adjust its predictions and decision-making processes to reflect the latest patterns and developments in the data. This adaptability ensures that supervised models remain relevant and effective in dynamic environments, allowing them to stay ahead of evolving trends and make informed decisions based on the most up-to-date information available.
Dependence on labelled data for training, which can be time-consuming and costly to acquire.
One significant drawback of supervised learning in artificial intelligence is its heavy reliance on labelled data for training purposes. Acquiring a sufficient amount of accurately labelled data can be a time-consuming and costly process, posing a challenge for many organisations and projects. The need for extensive human effort to annotate and categorise data points can slow down the development process and increase the overall expenses involved in training machine learning models. This dependence on labelled data not only adds complexity to the workflow but also limits the scalability of supervised learning systems, making it a notable con in the realm of artificial intelligence research and application.
Difficulty in handling unbalanced datasets where certain classes are underrepresented.
An inherent challenge of supervised learning in artificial intelligence is the difficulty in handling unbalanced datasets, where certain classes are significantly underrepresented compared to others. This imbalance can lead to biased models that favour majority classes, resulting in poor performance when predicting minority class instances. Addressing this issue requires careful consideration and implementation of techniques such as oversampling, undersampling, or using advanced algorithms designed to handle imbalanced data effectively. Failure to adequately manage unbalanced datasets can compromise the model’s ability to make accurate predictions across all classes, highlighting the importance of robust strategies in mitigating this con of supervised learning.
Risk of overfitting to the training data, leading to poor generalisation on unseen data.
One significant drawback of supervised learning in artificial intelligence is the risk of overfitting to the training data, which can result in poor generalisation on unseen data. Overfitting occurs when a model learns noise or irrelevant patterns present in the training dataset, rather than capturing the underlying relationships between features and labels. As a consequence, the model may perform exceptionally well on the training data but fail to make accurate predictions on new, unseen data. This limitation highlights the importance of carefully tuning model complexity and incorporating techniques such as regularisation to mitigate the risk of overfitting and improve generalisation performance in real-world applications.
Vulnerability to noise and outliers in the training dataset, impacting model performance.
One significant drawback of supervised learning in artificial intelligence is its vulnerability to noise and outliers present in the training dataset, which can severely impact the performance of the model. Noise refers to random variations or errors in the data, while outliers are data points that deviate significantly from the rest of the dataset. When a model is trained on data containing noise and outliers, it may learn patterns that do not accurately represent the underlying relationships in the data, leading to poor generalisation and decreased predictive accuracy. Addressing these challenges through robust preprocessing techniques and model selection is crucial to mitigate the negative effects of noise and outliers on supervised learning models.
Limited interpretability of complex models, making it challenging to understand how predictions are made.
In supervised learning, one significant drawback is the limited interpretability of complex models, such as deep neural networks and ensemble methods. These models often function as “black boxes,” where the internal workings and decision-making processes are not easily understood by humans. This lack of transparency poses challenges when trying to comprehend how predictions are made, which can be particularly problematic in critical applications like healthcare or finance, where understanding the rationale behind a decision is essential. As a result, stakeholders may struggle to trust these models fully, and it becomes difficult to identify and rectify any biases or errors within them. Efforts to improve model interpretability are ongoing, but achieving a balance between complexity and comprehensibility remains a challenging task in the field of artificial intelligence.
Ethical concerns related to biased or discriminatory outcomes if the training data is not representative or contains inherent biases.
Supervised learning in artificial intelligence can inadvertently result in biased or discriminatory outcomes if the training data is not representative of the broader population or contains inherent biases. When models are trained on datasets that reflect societal prejudices or skewed distributions, they may perpetuate these biases in their predictions. For instance, if a dataset used to train a hiring algorithm predominantly features candidates from a particular demographic group, the model might unfairly favour similar profiles in future predictions. This can lead to unequal treatment and reinforce existing disparities, raising significant ethical concerns. Ensuring diversity and fairness in training data is crucial to mitigate these issues and promote equitable AI systems.