The Power of Supply Chain Data Analytics
In today’s fast-paced and complex business environment, supply chain management plays a crucial role in the success of any organisation. The ability to effectively manage the flow of goods and services from raw materials to finished products is essential for meeting customer demands and maintaining a competitive edge. One key tool that has revolutionised supply chain management is data analytics.
What is Supply Chain Data Analytics?
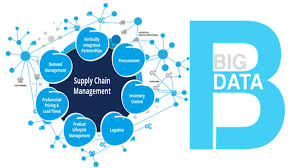
Supply chain data analytics involves the collection, analysis, and interpretation of data related to various aspects of the supply chain process. This includes information on inventory levels, production schedules, transportation routes, supplier performance, and customer demand. By leveraging advanced analytics tools and techniques, organisations can gain valuable insights into their supply chain operations and make informed decisions to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
The Benefits of Supply Chain Data Analytics
There are numerous benefits to implementing data analytics in supply chain management:
- Improved Forecasting: By analysing historical data and trends, organisations can better predict demand fluctuations and adjust their production and inventory levels accordingly.
- Enhanced Visibility: Data analytics provides real-time visibility into every stage of the supply chain, allowing for proactive problem-solving and faster decision-making.
- Optimised Operations: By identifying inefficiencies and bottlenecks in the supply chain process, organisations can streamline operations, reduce lead times, and improve overall performance.
- Cost Savings: Data analytics helps identify cost-saving opportunities such as optimising transportation routes, reducing excess inventory, and negotiating better supplier contracts.
Challenges of Implementing Supply Chain Data Analytics
While the benefits of supply chain data analytics are clear, there are challenges that organisations may face when implementing this technology:
- Data Quality: Ensuring that data is accurate, complete, and up-to-date is essential for meaningful analysis. Poor data quality can lead to inaccurate insights and decisions.
- Integration Complexity: Integrating data from multiple sources within the supply chain ecosystem can be complex. Organisations need robust systems in place to ensure seamless data flow.
- Skill Gap: Data analytics requires specialised skills and expertise. Organisations may need to invest in training or hire external talent to effectively leverage this technology.
The Future of Supply Chain Data Analytics
The future of supply chain management lies in harnessing the power of data analytics to drive innovation and competitiveness. As technology continues to advance, organisations that embrace data-driven decision-making will be better positioned to adapt to changing market dynamics and deliver superior customer experiences.
In conclusion, supply chain data analytics is a game-changer for businesses looking to optimise their operations, reduce costs, and stay ahead in today’s dynamic marketplace. By leveraging the insights gained from data analysis, organisations can transform their supply chains into strategic assets that drive growth and success.
Exploring Supply Chain Data Analytics: Key Questions and Insights
- What are the 5 common types of supply chain analytics?
- What is an example of supply chain analytics?
- What is the difference between supply chain analyst and data analyst?
- How do I get into supply chain analytics?
- How is big data analytics used in supply chain?
- Is supply chain analytics difficult?
- What is a data analytics supply chain?
- What is the main aim of supply chain analytics?
What are the 5 common types of supply chain analytics?
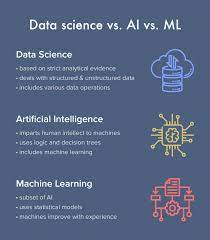
In the realm of supply chain data analytics, there are five common types of analytics that organisations frequently utilise to enhance their operations. These include descriptive analytics, which provide insights into past performance and current trends; diagnostic analytics, which help identify the root causes of issues within the supply chain; predictive analytics, which forecast future outcomes based on historical data and statistical models; prescriptive analytics, which offer recommendations on optimal actions to improve efficiency and decision-making; and finally, cognitive analytics, which leverage artificial intelligence and machine learning to uncover hidden patterns and provide advanced insights for strategic planning. Each type of supply chain analytics plays a unique role in empowering organisations to make informed decisions and drive continuous improvement in their supply chain processes.
What is an example of supply chain analytics?
An example of supply chain analytics is the use of predictive analytics to forecast demand for a particular product. By analysing historical sales data, market trends, and other relevant factors, organisations can predict future demand with greater accuracy. This enables them to adjust production schedules, inventory levels, and procurement strategies to meet customer needs efficiently while minimising excess inventory or stockouts. Supply chain analytics in this context not only optimises operational efficiency but also enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring products are available when and where they are needed most.
What is the difference between supply chain analyst and data analyst?
When it comes to supply chain data analytics, a common question that arises is the distinction between a supply chain analyst and a data analyst. While both roles involve working with data to derive insights and make informed decisions, the key difference lies in their focus areas. A supply chain analyst typically specialises in analysing data specific to the supply chain process, such as inventory levels, transportation routes, and supplier performance. On the other hand, a data analyst has a broader scope and may work with various types of data beyond just supply chain-related information. While both roles require strong analytical skills, understanding the nuances of supply chain operations sets a supply chain analyst apart from a general data analyst in the context of supply chain management.
How do I get into supply chain analytics?
For those looking to break into the field of supply chain analytics, there are several steps you can take to kickstart your career. Firstly, gaining a solid foundation in data analysis and statistical modelling is essential. Consider pursuing relevant courses or certifications to enhance your analytical skills. Additionally, familiarise yourself with supply chain management principles and industry trends to understand the context in which analytics is applied. Networking with professionals in the field and seeking out internships or entry-level positions in supply chain or data analytics can also provide valuable hands-on experience and insights. By continuously learning, building your skill set, and staying abreast of developments in supply chain analytics, you can position yourself for a successful career in this dynamic and growing field.
How is big data analytics used in supply chain?
Big data analytics is a powerful tool used in supply chain management to extract valuable insights from vast amounts of data generated at every stage of the supply chain process. By leveraging advanced analytics techniques and technologies, organisations can analyse complex data sets to identify patterns, trends, and correlations that traditional methods may overlook. Big data analytics helps in improving forecasting accuracy, enhancing inventory management, optimising transportation routes, identifying cost-saving opportunities, and enhancing overall operational efficiency. By harnessing the power of big data analytics, businesses can make informed decisions, mitigate risks, and stay competitive in today’s rapidly evolving supply chain landscape.
Is supply chain analytics difficult?
The complexity of implementing supply chain analytics depends on various factors, including the organisation’s existing data infrastructure, technological capabilities, and workforce skill set. While supply chain analytics can present challenges such as data quality issues, integration complexities, and the need for specialised expertise, with the right strategy and resources in place, organisations can overcome these obstacles and harness the power of data analytics to drive efficiency and innovation in their supply chain operations. Embracing a culture of continuous learning and adaptation is key to successfully navigating the complexities of supply chain analytics and reaping its benefits in today’s competitive business landscape.
What is a data analytics supply chain?
A data analytics supply chain refers to the use of data analytics tools and techniques to enhance visibility, efficiency, and decision-making within the supply chain process. By collecting and analysing data related to inventory levels, production schedules, transportation routes, supplier performance, and customer demand, organisations can gain valuable insights that help optimise operations and drive strategic improvements. Essentially, a data analytics supply chain empowers businesses to make informed decisions based on real-time data analysis, leading to better forecasting, cost savings, and overall performance enhancements throughout the supply chain ecosystem.
What is the main aim of supply chain analytics?
The main aim of supply chain analytics is to leverage data and advanced analytical tools to gain valuable insights into various aspects of the supply chain process. By analysing key performance indicators, trends, and patterns within the supply chain, organisations can make informed decisions to improve efficiency, reduce costs, enhance visibility, and ultimately drive better business outcomes. Supply chain analytics enables businesses to optimise operations, identify opportunities for improvement, and adapt quickly to changing market conditions, ensuring a competitive edge in today’s dynamic business landscape.