The Theory of Disruptive Innovation by Clayton Christensen
Disruptive innovation, a concept introduced by Harvard Business School professor Clayton Christensen in the mid-1990s, has since become a cornerstone in the world of business and technology. Christensen’s theory challenges traditional notions of how established companies can be overtaken by innovative newcomers.
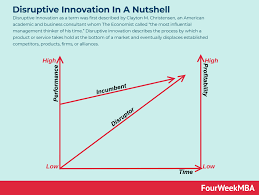
According to Christensen, disruptive innovation occurs when a smaller company with fewer resources introduces a product or service that initially may only cater to a niche market segment. Over time, this innovation improves and gains traction, eventually disrupting the existing market and displacing established competitors.
One key aspect of disruptive innovation is that it often targets underserved or overlooked customer segments with simpler, more affordable solutions. These innovations may not initially meet the performance standards set by existing products but gradually improve to the point where they become mainstream and preferred by customers.
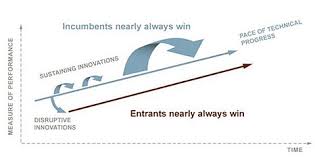
Christensen’s theory highlights the importance for incumbent companies to not only focus on sustaining innovations that cater to their current customer base but also to be aware of potential disruptive threats from emerging technologies and business models. Failure to adapt to disruptive innovations can lead to market obsolescence.
Many successful companies have fallen victim to disruptive innovations because they underestimated the impact of these new entrants on their industries. By understanding and embracing the principles of disruptive innovation, businesses can position themselves for long-term success in an ever-evolving marketplace.
In conclusion, Clayton Christensen’s theory of disruptive innovation serves as a reminder that staying competitive in today’s fast-paced world requires continuous adaptation and openness to change. By recognising and harnessing the power of disruptive innovations, companies can not only survive but thrive in an increasingly dynamic business environment.
Understanding Christensen’s Disruptive Innovation: Key Concepts and Examples
- What are the types of innovation according to Clayton Christensen?
- What are the two types of innovation that Christensen suggests have the potential to cause disruption?
- What is Christensen’s theory of disruptive innovation?
- What is disruptive innovation according to Christensen?
- What are Christensen two main types of disruptive innovation?
- What is an example of a disruptive innovation?
What are the types of innovation according to Clayton Christensen?
Clayton Christensen categorised innovation into two main types: sustaining and disruptive. Sustaining innovation involves improving existing products or services to meet the needs of current customers, often driven by incremental advancements. On the other hand, disruptive innovation introduces new solutions that initially may not meet the performance standards of established products but eventually redefine the market by targeting underserved customer segments with simpler, more affordable alternatives. By understanding and balancing these two types of innovation, businesses can navigate the complexities of a rapidly changing marketplace and stay ahead of the competition.
What are the two types of innovation that Christensen suggests have the potential to cause disruption?
Clayton Christensen suggests that there are two types of innovation with the potential to cause disruption: sustaining innovation and disruptive innovation. Sustaining innovation involves improving existing products or services to meet the needs of current customers, maintaining the status quo within an industry. On the other hand, disruptive innovation introduces new solutions that may initially target niche markets or underserved customers with simpler, more affordable offerings. Over time, these disruptive innovations have the capability to reshape industries by gradually gaining market share and displacing established competitors. Christensen’s distinction between these two types of innovation highlights the importance for businesses to not only focus on sustaining their current offerings but also to be aware of potential disruptive threats in order to stay competitive in a rapidly changing business landscape.
What is Christensen’s theory of disruptive innovation?
Christensen’s theory of disruptive innovation, a concept pioneered by Harvard Business School professor Clayton Christensen, revolves around the idea that smaller, innovative companies can disrupt established industries by introducing simpler, more affordable solutions that initially cater to niche markets. These disruptive innovations gradually improve in performance and gain mainstream acceptance, eventually displacing incumbent competitors. Christensen’s theory emphasises the importance of incumbent companies not only focusing on sustaining innovations but also being aware of potential disruptive threats from emerging technologies and business models. By understanding and adapting to the principles of disruptive innovation, businesses can navigate the evolving marketplace landscape and position themselves for long-term success.
What is disruptive innovation according to Christensen?
Disruptive innovation, as defined by Clayton Christensen, refers to the process by which smaller and often overlooked companies introduce new products or services that initially cater to niche markets with simpler and more affordable solutions. Over time, these innovations improve and gain traction, eventually disrupting established markets and displacing incumbent competitors. Christensen’s theory emphasises the importance of recognising the potential of disruptive technologies and business models in reshaping industries, urging companies to adapt and innovate to stay ahead in a rapidly changing business landscape.
What are Christensen two main types of disruptive innovation?
Clayton Christensen identified two main types of disruptive innovation: low-end disruption and new-market disruption. Low-end disruption involves introducing a simpler, more affordable product or service targeted at underserved customers at the lower end of the market. New-market disruption, on the other hand, focuses on creating entirely new markets or customer segments by offering innovative solutions that address unmet needs or create new demand. By understanding these two types of disruptive innovation, businesses can better anticipate and respond to emerging threats and opportunities in their industries.
What is an example of a disruptive innovation?
An example of a disruptive innovation can be seen in the rise of digital streaming services in the entertainment industry. Initially targeting a niche market segment with lower-quality streaming options, companies like Netflix disrupted the traditional video rental and broadcast television industries. By offering a more convenient, affordable, and on-demand viewing experience, these digital platforms gradually gained popularity and eventually reshaped the way audiences consume content, leading to a significant shift in the industry landscape. This example illustrates how disruptive innovations can start small but ultimately have a transformative impact on established markets.