The Importance of Quantitative Statistical Analysis
Quantitative statistical analysis plays a crucial role in various fields, including science, business, economics, and social sciences. It involves the use of mathematical and statistical methods to analyse data and draw meaningful conclusions. By quantifying data and applying statistical techniques, researchers can uncover patterns, trends, and relationships that help in making informed decisions.
Key Aspects of Quantitative Statistical Analysis
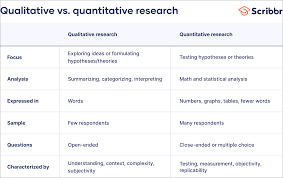
One of the key aspects of quantitative statistical analysis is the use of numerical data. Researchers collect data through surveys, experiments, or observations and then convert this data into numerical form for analysis. This allows for precise measurement and comparison of variables.
Statistical analysis techniques such as descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, regression analysis, and hypothesis testing are commonly used to interpret quantitative data. Descriptive statistics provide an overview of the data distribution, while inferential statistics help in making predictions or generalisations based on sample data.
Applications of Quantitative Statistical Analysis
In the field of business, quantitative statistical analysis is used for market research, financial forecasting, performance evaluation, and risk assessment. By analysing numerical data related to sales figures, customer demographics, or stock prices, businesses can make strategic decisions to improve their operations.
In scientific research, quantitative statistical analysis is essential for testing hypotheses, identifying patterns in experimental data, and drawing conclusions based on evidence. Researchers use statistical tools to analyse results from experiments and determine the significance of their findings.
Challenges in Quantitative Statistical Analysis
While quantitative statistical analysis offers valuable insights into complex datasets, it also poses challenges related to data quality, sample size determination, assumptions validation, and interpretation of results. Researchers must carefully design their studies and choose appropriate statistical methods to ensure the reliability and validity of their findings.
Conclusion
In conclusion, quantitative statistical analysis is a powerful tool that enables researchers to extract meaningful information from numerical data. By applying mathematical models and statistical techniques to analyse datasets, researchers can gain valuable insights that drive decision-making processes across various disciplines. Understanding the principles of quantitative statistical analysis is essential for anyone seeking to make informed decisions based on empirical evidence.
Understanding Quantitative Statistical Analysis: Methods, Examples, and Types
- What is an example of quantitative analysis?
- What is a quantitative method of statistical analysis?
- What is quantitative analysis examples?
- What are the 4 types of quantitative analysis?
- What are the statistical methods to analyze quantitative data?
What is an example of quantitative analysis?
Quantitative analysis involves the use of numerical data and statistical methods to examine and interpret trends, patterns, and relationships within a dataset. An example of quantitative analysis is conducting a survey to collect data on customer satisfaction ratings for a product or service. By assigning numerical values to responses and analysing the data using statistical techniques such as mean, median, and standard deviation, businesses can gain insights into customer preferences and make informed decisions to improve their offerings. This example illustrates how quantitative analysis enables organisations to quantify feedback and derive actionable conclusions from numerical data.
What is a quantitative method of statistical analysis?
A quantitative method of statistical analysis involves the use of numerical data and mathematical techniques to interpret and draw conclusions from datasets. This approach focuses on quantifying variables and relationships between them to uncover patterns, trends, and associations within the data. By applying statistical methods such as descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, regression analysis, and hypothesis testing, researchers can analyse numerical data systematically to make informed decisions and predictions based on empirical evidence. Quantitative statistical analysis is a fundamental tool in research across various fields, providing a structured framework for analysing data and deriving meaningful insights through rigorous mathematical and statistical processes.
What is quantitative analysis examples?
Quantitative analysis examples encompass a wide range of applications across different fields. In finance, quantitative analysis involves using mathematical models and statistical tools to evaluate investment opportunities, predict market trends, and manage risk. In healthcare, quantitative analysis is used to analyse clinical trial data, track patient outcomes, and identify patterns in disease prevalence. In social sciences, quantitative analysis helps researchers examine survey responses, conduct experiments, and draw statistical inferences about human behaviour. These examples highlight the versatility and importance of quantitative analysis in generating insights and making informed decisions based on numerical data.
What are the 4 types of quantitative analysis?
In the realm of quantitative statistical analysis, there are four primary types of quantitative analysis techniques commonly utilised: descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, regression analysis, and hypothesis testing. Descriptive statistics involve summarising and presenting data in a meaningful way to describe characteristics of a dataset. Inferential statistics focus on making predictions or inferences about a population based on sample data. Regression analysis examines the relationship between variables, while hypothesis testing involves evaluating hypotheses using statistical methods to determine the significance of results. Each type of quantitative analysis serves a distinct purpose in extracting valuable insights from data and informing decision-making processes.
What are the statistical methods to analyze quantitative data?
When considering the question “What are the statistical methods to analyse quantitative data?” in the context of quantitative statistical analysis, various statistical methods can be employed. Commonly used techniques include descriptive statistics, which summarise and describe the characteristics of a dataset, inferential statistics, which help in making predictions or generalisations based on sample data, regression analysis, which examines relationships between variables, and hypothesis testing, which assesses the significance of findings. By utilising these statistical methods effectively, researchers can gain valuable insights from quantitative data and draw meaningful conclusions to inform decision-making processes.