The Power of Data Analysis
Data analysis is the process of inspecting, cleansing, transforming, and modelling data with the goal of discovering useful information, informing conclusions, and supporting decision-making. In today’s digital age, data analysis has become a crucial tool for businesses, researchers, and organisations across various industries.
Importance of Data Analysis
Effective data analysis enables businesses to make informed decisions based on facts rather than intuition. By analysing large datasets, organisations can identify trends, patterns, and correlations that may not be immediately apparent. This insight allows businesses to optimise processes, improve efficiency, and gain a competitive edge in the market.
Types of Data Analysis
There are several types of data analysis techniques used depending on the nature of the data and the objectives of the analysis:
- Descriptive Analysis: Describes what has happened in the past based on historical data.
- Diagnostic Analysis: Seeks to determine why something happened by identifying causal relationships.
- Predictive Analysis: Predicts future outcomes based on historical data and statistical algorithms.
- Prescriptive Analysis: Recommends actions to achieve a desired outcome based on predictive models.
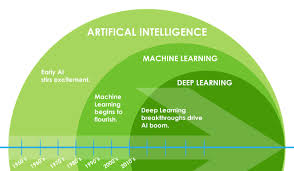
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in Data Analysis
Artificial intelligence (AI) plays a significant role in enhancing data analysis capabilities. Machine learning algorithms can process vast amounts of data at high speeds to identify complex patterns and make accurate predictions. AI-powered analytics tools are revolutionising how businesses extract insights from their data, enabling them to make more informed decisions in real time.
Challenges in Data Analysis
Despite its numerous benefits, data analysis also presents challenges such as ensuring data quality, dealing with unstructured data sources, and maintaining data privacy and security. Overcoming these challenges requires robust processes, advanced technologies, and skilled professionals who can interpret results accurately.
In Conclusion
Data analysis is a powerful tool that empowers organisations to unlock valuable insights from their data assets. By leveraging advanced analytics techniques and technologies such as AI, businesses can gain a deeper understanding of their operations, customers, and market dynamics. In today’s data-driven world, effective data analysis is key to driving innovation and achieving sustainable growth.
Comprehensive Guide to Data Analysis: Common Questions and Methods Explained
- What are the three ways of data analysis?
- What is analysis of data and examples?
- What is analysis of data example?
- What are methods of data analysis?
- What is analysis of data in research?
- What is an example of data analysis?
- What is data analysis with example?
- What is analysis of data?
- What are the 3 steps to analyzing data?
What are the three ways of data analysis?
Data analysis encompasses various methods to derive meaningful insights from data. When it comes to the question of the three ways of data analysis, three key approaches stand out: descriptive analysis, diagnostic analysis, and predictive analysis. Descriptive analysis focuses on summarising and interpreting historical data to understand what has happened in the past. Diagnostic analysis delves deeper into why certain events occurred by identifying causal relationships within the data. Predictive analysis, on the other hand, uses statistical algorithms and machine learning techniques to forecast future outcomes based on historical data patterns. These three distinct methods play a crucial role in uncovering trends, patterns, and correlations within datasets to inform decision-making processes across different industries.
What is analysis of data and examples?
The analysis of data refers to the systematic process of examining, interpreting, and drawing meaningful insights from datasets to uncover patterns, trends, and relationships. By applying various statistical and computational techniques, data analysis helps extract valuable information that can guide decision-making and drive business strategies. Examples of data analysis include performing regression analysis to understand the relationship between variables, conducting cluster analysis to group similar data points together, and using sentiment analysis to gauge customer opinions from text data. These examples showcase the versatility and importance of data analysis in extracting actionable intelligence from raw data.
What is analysis of data example?
Data analysis is the process of examining, interpreting, and deriving meaningful insights from datasets to inform decision-making. An example of data analysis could be a retail company analysing sales data to identify trends in customer purchasing behaviour. By studying patterns in sales figures, such as which products are selling well during specific seasons or promotions, the company can make informed decisions on inventory management, pricing strategies, and marketing campaigns to maximise profitability and enhance customer satisfaction. This demonstrates how data analysis can provide valuable insights that drive strategic business actions and improvements.
What are methods of data analysis?
When it comes to the analysis of data, there are various methods that can be employed to extract meaningful insights and draw conclusions. Common methods of data analysis include descriptive analysis, which summarises and describes data patterns; diagnostic analysis, which aims to identify the causes of certain phenomena; predictive analysis, which uses historical data to make informed predictions about future trends; and prescriptive analysis, which recommends specific actions based on analytical findings. Each method serves a unique purpose in uncovering valuable information from datasets and guiding decision-making processes across different industries and disciplines.
What is analysis of data in research?
The analysis of data in research refers to the systematic process of examining, interpreting, and drawing meaningful conclusions from collected data sets. It involves applying statistical methods, data mining techniques, and other analytical tools to uncover patterns, trends, and relationships within the data. Data analysis in research is essential for researchers to validate hypotheses, identify significant findings, and make informed decisions based on empirical evidence. By rigorously analysing data, researchers can extract valuable insights that contribute to the advancement of knowledge in their respective fields and support evidence-based conclusions.
What is an example of data analysis?
Data analysis encompasses a wide range of techniques and applications, with one common example being the analysis of sales data in retail. For instance, a retail business may collect data on customer purchases, including items bought, purchase frequency, and customer demographics. By analysing this data, the business can identify popular products, peak sales periods, customer preferences, and trends over time. This information enables the business to make informed decisions such as adjusting inventory levels, launching targeted marketing campaigns, or introducing new product lines to maximise profitability and enhance the overall customer experience.
What is data analysis with example?
Data analysis is the systematic process of examining, cleaning, transforming, and interpreting data to uncover meaningful insights and patterns. An example of data analysis could involve a retail company analysing sales data to identify trends in customer purchasing behaviour. By examining factors such as product preferences, buying patterns, and seasonal variations, the company can make informed decisions on inventory management, marketing strategies, and pricing adjustments. Through data analysis, businesses can gain valuable insights that drive strategic decision-making and ultimately improve overall performance and profitability.
What is analysis of data?
The analysis of data refers to the systematic process of examining, interpreting, and deriving meaningful insights from raw data to uncover patterns, trends, and relationships. It involves applying various statistical and computational techniques to transform data into actionable information that can be used to make informed decisions. Data analysis plays a crucial role in understanding complex datasets, identifying key metrics, and extracting valuable knowledge that can drive business strategies and outcomes. By delving into the depths of data through analysis, organisations can gain a deeper understanding of their operations, customers, and market dynamics, ultimately leading to improved efficiency and informed decision-making.
What are the 3 steps to analyzing data?
When it comes to analysing data, there are typically three key steps involved in the process. The first step is data collection, where relevant information is gathered from various sources such as databases, surveys, or sensors. Next comes data processing, which involves cleaning and organising the collected data to ensure accuracy and consistency. Finally, the third step is data analysis itself, where techniques such as statistical analysis, machine learning, or visualisation are applied to extract meaningful insights and draw conclusions from the processed data. By following these three fundamental steps – data collection, processing, and analysis – organisations can harness the power of their data to make informed decisions and drive business growth.