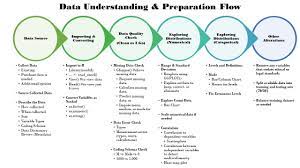
Exploratory Statistics: Unveiling Insights from Data
Exploratory statistics is a powerful tool in the field of data analysis that allows researchers and analysts to uncover patterns, trends, and relationships within a dataset. Rather than starting with a specific hypothesis, exploratory statistics focuses on exploring the data itself to gain a deeper understanding of its underlying structure.
One of the key goals of exploratory statistics is to visualise data in various forms, such as histograms, scatter plots, box plots, and more. These visualisations help analysts identify outliers, understand the distribution of variables, and detect potential correlations between different factors.
Descriptive statistics play a crucial role in exploratory analysis by summarising the main characteristics of the dataset. Measures like mean, median, mode, standard deviation, and range provide valuable insights into the central tendency and variability of the data.
Another essential aspect of exploratory statistics is hypothesis generation. By examining patterns in the data and identifying interesting relationships, researchers can formulate new hypotheses for further investigation. This iterative process of exploration often leads to unexpected discoveries and new research directions.
Exploratory statistics is not limited to numerical data but can also be applied to categorical variables through techniques like frequency tables, bar charts, and chi-square tests. By exploring both quantitative and qualitative aspects of the dataset, analysts can gain a comprehensive understanding of the underlying phenomena.
In conclusion, exploratory statistics serves as a vital first step in any data analysis project by providing an initial glimpse into the hidden patterns within a dataset. By leveraging visualisations, descriptive statistics, hypothesis generation, and more, analysts can unveil valuable insights that lay the foundation for further exploration and hypothesis testing.
7 Essential Tips for Effective Exploratory Data Analysis
- Start by summarising your data with descriptive statistics such as mean, median, mode, and standard deviation.
- Visualise your data using histograms, box plots, scatter plots, or other suitable graphs to identify patterns and trends.
- Check for outliers in your data that may skew your analysis or indicate errors in data collection.
- Explore relationships between variables using correlation analysis to understand how they are related to each other.
- Consider conducting hypothesis tests to make inferences about the population based on sample data.
- Use measures of central tendency and variability to better understand the distribution of your data.
- Document your exploratory analysis process thoroughly to ensure reproducibility and transparency.
Start by summarising your data with descriptive statistics such as mean, median, mode, and standard deviation.
Beginning your exploratory statistical analysis by summarising your data with descriptive statistics, including measures like mean, median, mode, and standard deviation, is a crucial step in understanding the central tendencies and variability within your dataset. These summary statistics provide valuable insights into the distribution of your data, helping you identify patterns and outliers that may influence further analysis. By starting with a solid foundation of descriptive statistics, you can gain a clearer picture of the underlying characteristics of your data and make informed decisions about the next steps in your exploration.
Visualise your data using histograms, box plots, scatter plots, or other suitable graphs to identify patterns and trends.
Visualising data through histograms, box plots, scatter plots, or other appropriate graphs is a crucial tip in exploratory statistics. These visual representations offer a clear and intuitive way to explore the underlying patterns and trends within a dataset. By examining the distribution of variables, detecting outliers, and identifying potential relationships between factors, analysts can gain valuable insights that may not be apparent from raw data alone. Visualisation plays a key role in uncovering hidden patterns and guiding further analysis, making it an essential step in the exploratory statistics process.
Check for outliers in your data that may skew your analysis or indicate errors in data collection.
When conducting exploratory statistics, it is essential to check for outliers in your data that could potentially distort your analysis or reveal errors in data collection. Outliers are data points that significantly deviate from the rest of the dataset and can have a substantial impact on statistical measures such as the mean and standard deviation. By identifying and examining outliers, researchers can gain insights into potential data quality issues, anomalous observations, or interesting patterns that warrant further investigation. Addressing outliers appropriately is crucial to ensuring the accuracy and reliability of the analysis results.
Explore relationships between variables using correlation analysis to understand how they are related to each other.
When conducting exploratory statistics, it is essential to explore relationships between variables through correlation analysis. By examining the strength and direction of relationships between different factors, analysts can gain valuable insights into how variables are interrelated. Correlation analysis helps to uncover patterns, dependencies, and potential causal links within the dataset, enabling a deeper understanding of the underlying connections between variables. This approach not only provides a comprehensive view of the data but also lays the groundwork for further analysis and hypothesis testing in research and decision-making processes.
Consider conducting hypothesis tests to make inferences about the population based on sample data.
When delving into exploratory statistics, it is essential to consider conducting hypothesis tests to draw meaningful inferences about the population from sample data. Hypothesis testing allows researchers to assess the significance of observed patterns or relationships in the data and determine whether these findings are likely due to chance or represent true effects within the population. By applying rigorous statistical tests, analysts can confidently make informed decisions and generalisations based on their sample data, providing valuable insights into the broader context of the research question at hand.
Use measures of central tendency and variability to better understand the distribution of your data.
Utilising measures of central tendency, such as the mean, median, and mode, along with measures of variability like standard deviation and range, is essential in exploratory statistics to gain a comprehensive understanding of the distribution of your data. These statistical metrics provide valuable insights into the typical values within the dataset (central tendency) as well as how spread out or clustered the data points are around the central values (variability). By analysing these measures, researchers can assess the shape and characteristics of the data distribution, helping them identify patterns, outliers, and potential relationships that may influence further analysis and decision-making processes.
Document your exploratory analysis process thoroughly to ensure reproducibility and transparency.
Documenting your exploratory analysis process thoroughly is essential to ensure reproducibility and transparency in your research. By carefully recording each step taken, including data cleaning, visualisations created, statistical techniques applied, and insights gained, you not only make your work more accessible to others but also enable yourself to replicate the analysis in the future. Transparent documentation allows for peer review, validation of results, and building upon existing research findings. It also promotes good research practices and fosters trust in the validity of your exploratory statistics outcomes.